Introduction
Biometric authentication is revolutionizing the way we verify identities, offering a seamless blend of security and convenience. This innovative approach to identity verification harnesses biological measurements, ranging from fingerprints to facial recognition, to ensure that individuals are precisely who they say they are. The allure of biometrics lies not only in their accuracy but also in their efficiency.
For instance, unlocking a smartphone is now a swift gesture of placing a finger on a sensor or glancing at a camera, a significant upgrade over the traditional password entry. This quest for speed, even if it shaves off mere seconds, resonates with consumers' desires for immediate results. Reflecting this trend, the biometrics scan software market has witnessed robust growth, with valuation soaring to an impressive $1 billion as of 2021.
Despite the evident advantages, there's a palpable sense of caution among users regarding the potential risks associated with biometrics. Nevertheless, the industry continues to evolve, with ongoing research delving into various biometric systems to refine and advance the technology further. Looking ahead, experts forecast a digital identity ecosystem underpinned by biometrics, digital identity wallets, and public-key cryptography, indicating a transformative future for the field.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is revolutionizing the way we verify identities, offering a seamless blend of security and convenience. This innovative approach to identity verification harnesses biological measurements—ranging from fingerprints to facial recognition—to ensure that individuals are precisely who they say they are.
The allure of biometrics lies not only in their accuracy but also in their efficiency; for instance, unlocking a smartphone is now a swift gesture of placing a finger on a sensor or glancing at a camera, a significant upgrade over the traditional password entry. This quest for speed, even if it shaves off mere seconds, resonates with consumers' desires for immediate results.
Reflecting this trend, the biometrics scan software market has witnessed robust growth, with valuation soaring to an impressive $1 billion as of 2021. Despite the evident advantages, there's a palpable sense of caution among users regarding the potential risks associated with biometrics. Nevertheless, the industry continues to evolve, with research by T. Sabhanayagam and colleagues in 2018 delving into various biometric systems, analyzing different fingerprint identification methods to refine and advance the technology further. Looking ahead, experts like Alan Goode forecast a digital identity ecosystem underpinned by biometrics, digital identity wallets, and public-key cryptography, indicating a transformative future for the field.
Advantages of Biometric Authentication
The evolution of biometric technology has significantly outpaced traditional security measures like passwords or Pins. Unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints and facial patterns are not only difficult to duplicate, but they also provide a formidable barrier against unauthorized access.
In fact, the convenience of biometric authentication is evident in everyday scenarios, such as unlocking smartphones, where a simple touch or glance replaces the need for cumbersome passwords. This shift toward biometrics is reflected in the industry's impressive growth, with the biometric scan software market reaching a value of approximately $1.0 billion as of 2021.
Users benefit from a seamless experience, as biometric authentication shortens the time spent on verifying identity and eradicates common obstacles such as password recovery. Despite the convenience and enhanced security, it's important to acknowledge the apprehensions that some individuals have regarding the potential risks associated with biometric data. Nonetheless, the adoption of biometric techniques continues to rise, driven by the demand for efficiency and the promise of a more secure authentication landscape.

Types of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is revolutionizing the way we verify identities, particularly in the realm of global travel and immigration. This technology, which includes fingerprint, facial, iris, and voice recognition, harnesses our unique physical and behavioral characteristics to create a more secure and efficient ID verification process.
Fingerprint recognition taps into the distinctive patterns on our fingertips, while facial recognition employs advanced algorithms to analyze our facial structures. Iris recognition capitalizes on the singular patterns of one's iris, and voice recognition distinguishes us by the specific qualities of our speech.
Additional methods such as palm and vein recognition, along with behavioral biometrics like signature and keystroke dynamics, further enhance the security arsenal. These advancements, propelled by machine learning and computer vision, are not only reducing the margin for error but are also streamlining the authentication process, making it quicker and more reliable—a boon for the integrity of passport recognition. As the digital identity landscape evolves, incorporating biometrics alongside digital identity wallets and public-key cryptography, the way we travel is being transformed to be faster and safer. According to Goode Intelligence, these developments are set to shape the future of digital identity through 2029 and beyond, making now the perfect time to explore the possibilities that biometric authentication has to offer for secure and hassle-free travels.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication stands as a cornerstone of modern security, leveraging unique biological measurements—like fingerprints and facial recognition—to accurately identify individuals. This technology not only bolsters security by making unauthorized access exceedingly challenging but also streamlines the identification process.
Where traditional methods such as passwords or Pins falter, biometric authentication shines, offering a level of reliability that thwarts identity theft and fraud more effectively. The convenience of biometric systems is evident in everyday scenarios, such as swiftly unlocking smartphones with a simple touch or glance—saving precious seconds that add up.
This quest for efficiency has propelled the biometrics scan software industry to impressive heights, with its market value hitting an estimated $1.0 billion in 2021. Moreover, industry experts like Alan Goode, CEO of Goode Intelligence, underscore the pivotal role biometrics play in the evolving digital identity landscape. As part of a broader ecosystem encompassing digital identity wallets and public-key cryptography, biometric authentication is poised to redefine user experiences, offering a seamless blend of security and practicality. However, despite the clear advantages, a cautious approach persists among consumers, mindful of the potential risks associated with biometrics.
Risks and Challenges of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication, while enhancing security and convenience, carries inherent risks that must be meticulously managed. The privacy of individuals is paramount, as biometrics involve sensitive personal data like fingerprints and facial scans. Organizations are tasked with implementing stringent security protocols to defend against unauthorized access or exploitation of this information.
Moreover, biometric systems are not infallible; they can produce false positives or negatives, occasionally misidentifying individuals or rejecting authentic traits, which undermines system efficacy and user trust. The challenge of data compromise is also significant. Robust encryption and secure storage are critical to protect biometric data from theft or unauthorized use.
In light of recent legislative developments, such as Paraguay's Law No. 7177/2023 aimed at digital modernization, the importance of balancing technological advancements with the protection of fundamental privacy rights is underscored. As per Pew Research Center's findings, public concern over personal data usage by companies and government has intensified, signaling a pressing need for transparent and secure data management practices.
Use Cases for Biometric Authentication
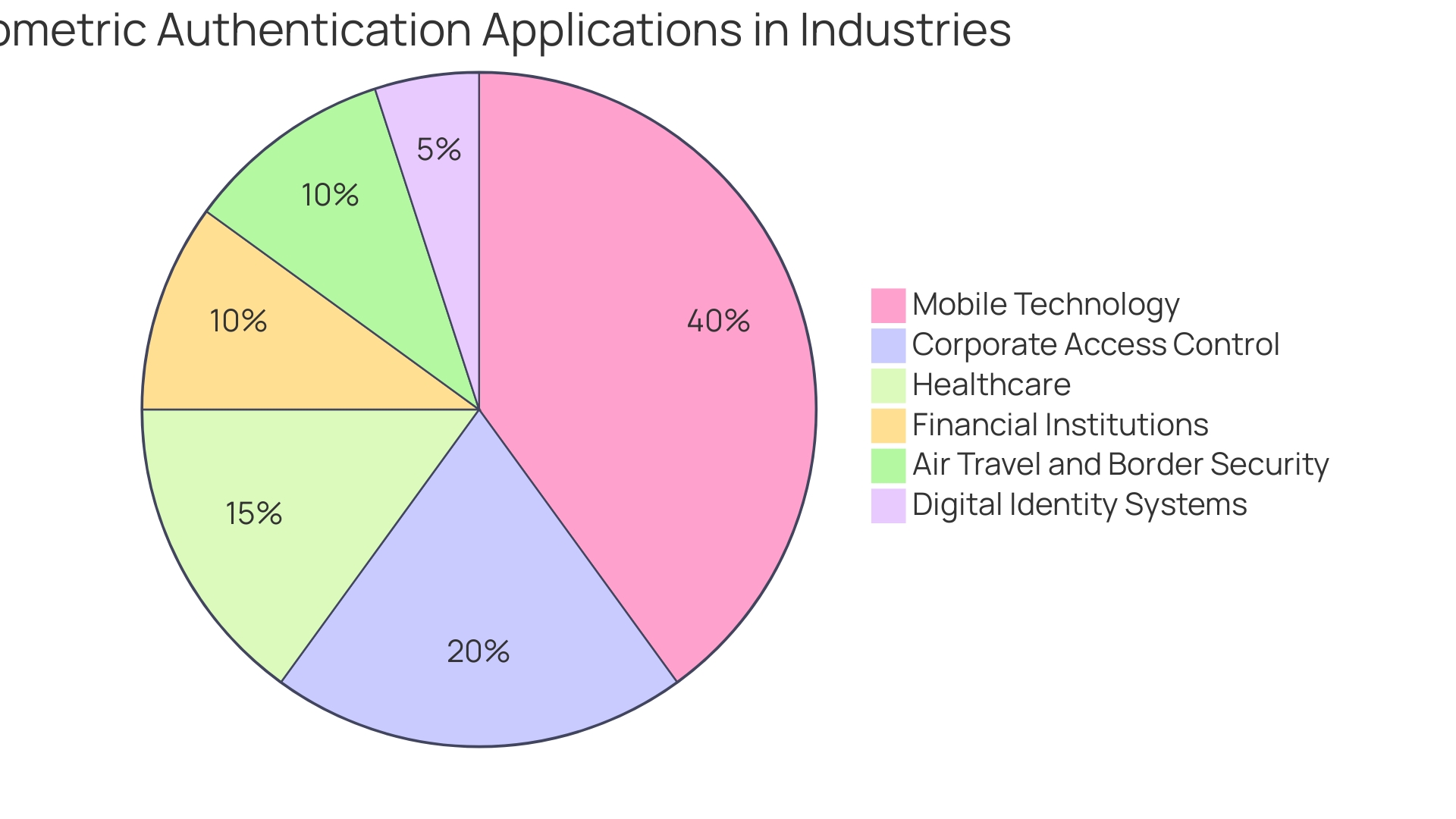
Biometric authentication, which encompasses biological measurements for individual identification, is revolutionizing efficiency across industries. In the realm of mobile technology, the convenience is palpable; fingerprint and facial recognition technologies have replaced the cumbersome process of password inputs, allowing users to unlock devices in mere seconds.
This pursuit of efficiency is mirrored in the biometrics scan software market's impressive growth, hitting the $1.0 billion mark in 2021. In the corporate world, access control systems have been elevated through biometric technology, ensuring only authorized personnel can enter sensitive areas, thereby bolstering security.
This technology is particularly vital in healthcare, where it serves a dual purpose: safeguarding patient records and verifying patient identities, thus preventing medical errors. Similarly, financial institutions leverage biometrics to secure online banking, curbing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
Air travel and border security have not been left behind. Airports now employ biometric systems to expedite immigration checks while maintaining stringent security standards. As the industry evolves, so does the understanding of biometric applications, with research like that of T. Sabhanayagam et al. (2018) offering valuable insights into the future of biometric technologies in areas such as ATM systems. Furthermore, digital identity systems are increasingly integrating biometrics as a foundational technology, with predictions of digital identity wallets and public-key cryptography becoming mainstream by 2029, as highlighted by Alan Goode, a leading expert in digital identity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biometric authentication is revolutionizing identity verification by harnessing biological measurements like fingerprints and facial recognition. It offers a seamless blend of security and convenience, with tasks like unlocking smartphones becoming quick and efficient.
The market for biometrics scan software has witnessed robust growth, reflecting the demand for immediate results. Despite potential risks, ongoing research is refining and advancing biometric technology.
Experts predict a transformative future for the field, with a digital identity ecosystem supported by biometrics, digital identity wallets, and public-key cryptography. Biometric authentication provides significant advantages over traditional security measures.
It offers enhanced security through unique physical characteristics that are difficult to duplicate. Additionally, it streamlines the identification process and eliminates obstacles like password recovery.
There are various types of biometric authentication, including fingerprint, facial, iris, and voice recognition. Advances in machine learning and computer vision make the authentication process quicker and more reliable.
However, privacy concerns and data compromise pose challenges that must be addressed through strict security protocols. Biometric authentication finds use cases across industries from mobile technology to healthcare and financial institutions. It also plays a vital role in air travel and border security. In conclusion, biometric authentication offers a transformative future for identity verification. Advances in technology continue to refine this innovative approach to security. With its ability to provide both security and convenience, biometrics will shape the future of digital identity ecosystems worldwide.





