Introduction
In an age where mobile devices are integral to daily life, the rise of mobile phishing presents a pressing challenge for users and organizations alike. Unlike traditional phishing, which often relies on email, mobile phishing exploits the very applications that make smartphones indispensable.
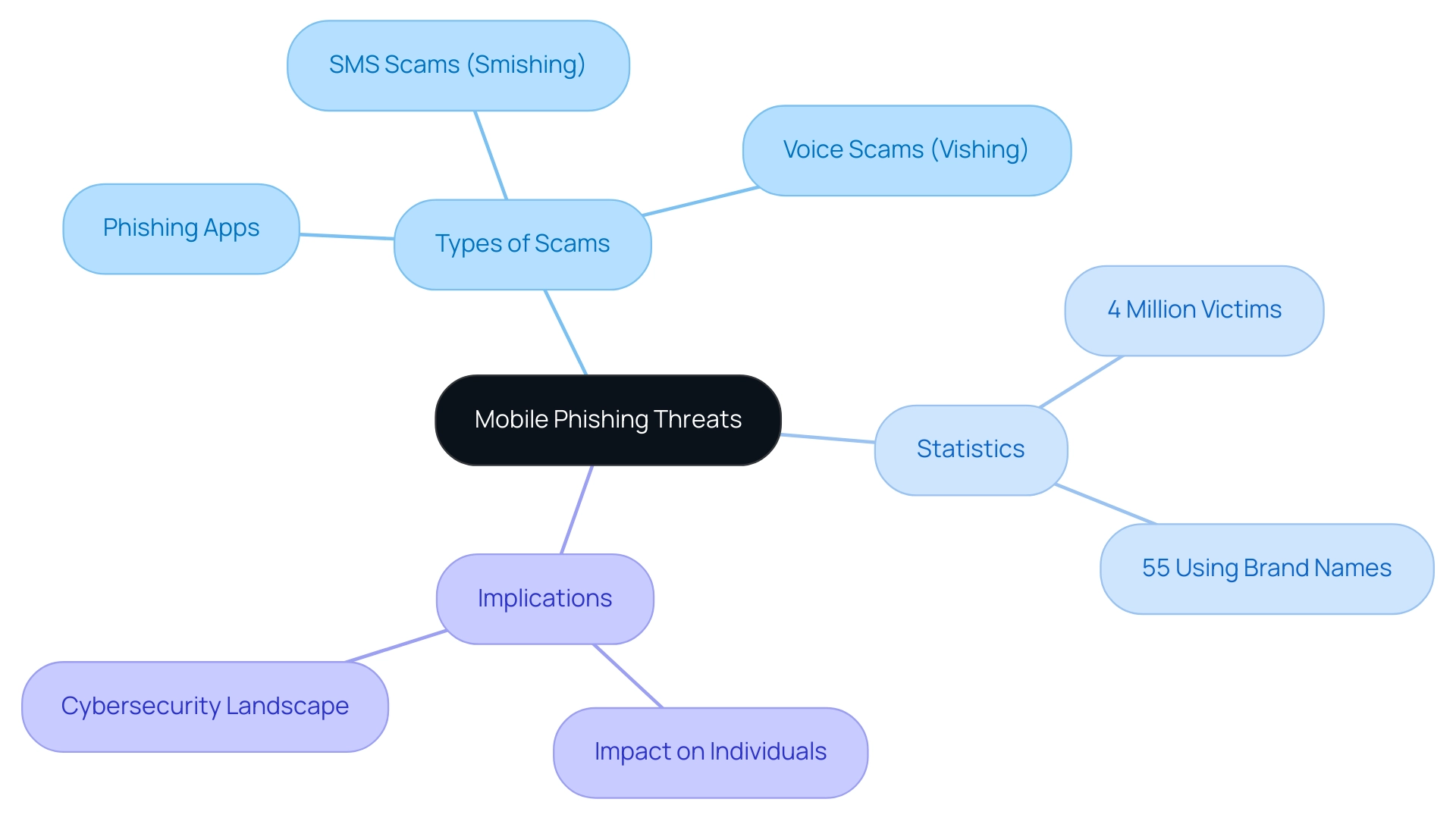
Cybercriminals are increasingly sophisticated, crafting malicious apps that masquerade as legitimate services, tricking users into revealing sensitive information. The alarming statistics reveal a surge in these attacks, with millions falling prey to tactics such as SMS phishing and voice phishing.
As the landscape of cyber threats evolves, understanding how these scams operate and recognizing the red flags is crucial for safeguarding personal and organizational data. This article delves into the intricacies of mobile phishing, outlines the most notorious phishing apps to be wary of, and provides actionable strategies to protect against these insidious threats.
Understanding Mobile Phishing: The New Frontier of Cyber Threats
As smartphone usage continues to rise, online deceit has surfaced as a significant issue within the cybersecurity realm. Distinct from conventional scams that primarily operate through email channels, phishing mobile apps exploit the accessibility of mobile applications to ensnare users. Cybercriminals deploy phishing mobile apps that are designed to mimic legitimate services, tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal identification.
The FBI has notably informed the public about the increase in fraud and scam schemes, particularly in connection with the US Student Loan Forgiveness process, emphasizing the urgency of this issue. According to recent statistics, over 4 million individuals have fallen prey to scam attacks, a trend that shows no signs of abating. This alarming rise is underscored by the fact that 55% of fraudulent attempts leverage established brand names to gain credibility, with LinkedIn being the most frequently imitated brand, accounting for 52% of such attacks.
Experts from the threat actor group Scattered Spider emphasize that tactics such as SMS scams (smishing) and voice scams (vishing) are increasingly used to solicit credentials, which are often exploited in subsequent calls to help desks. These support personnel may be persuaded to grant password and multi-factor authentication (MFA) resets for targeted accounts. Furthermore, IBM's research emphasizes that fraudulent schemes are responsible for 41% of all cyber incidents, serving as a common entry point for more severe threats like ransomware.
Grasping the mechanics of phishing mobile apps is crucial for individuals to identify and lessen these risks, particularly as cybercriminals consistently enhance their methods to exploit weaknesses in mobile software.
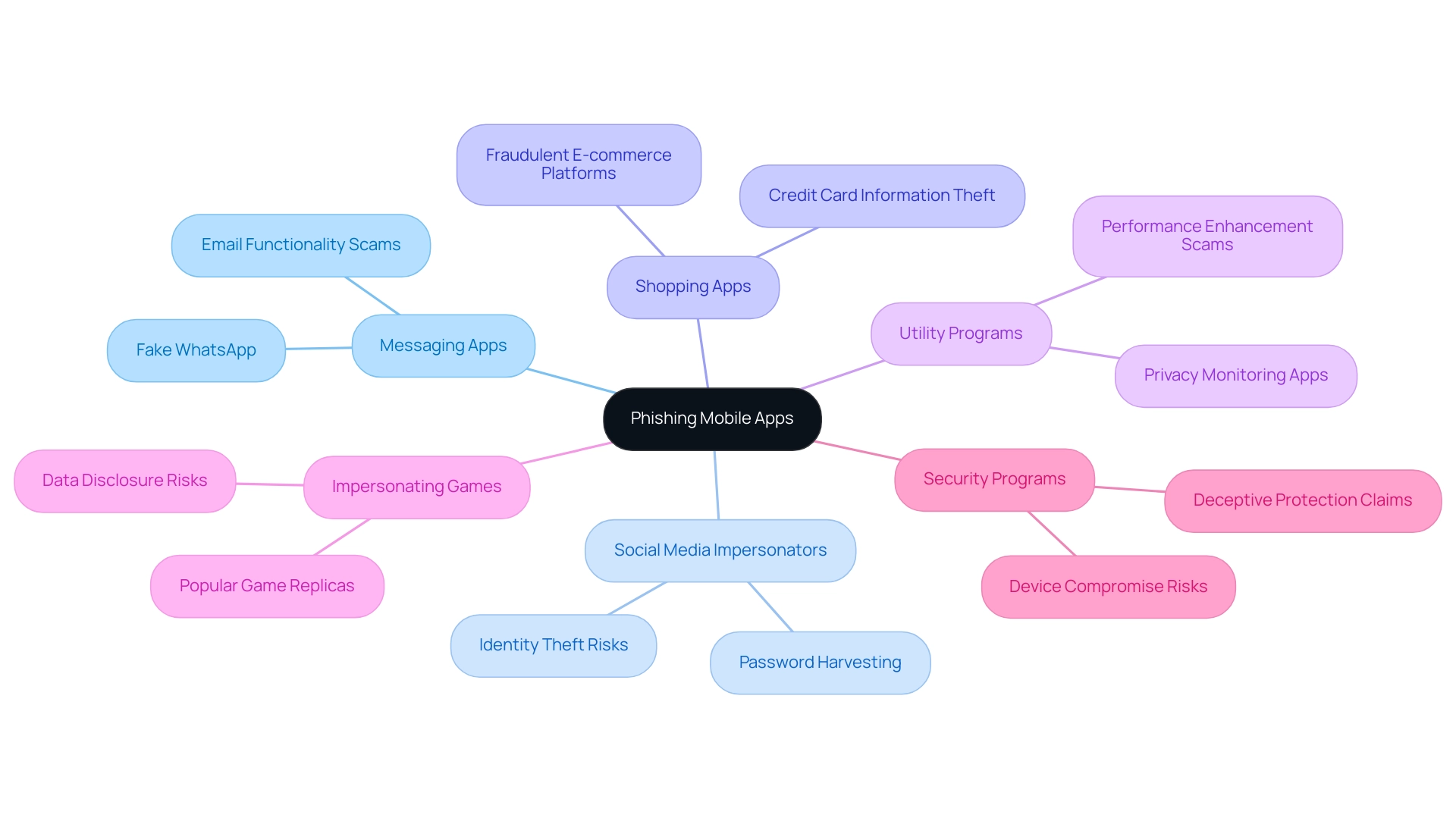
Top 10 Phishing Mobile Apps to Be Aware Of
- Phishing mobile apps such as fake WhatsApp disguise themselves as popular messaging platforms, specifically designed to trick individuals into providing sensitive information, including personal messages and contacts.
Phishing mobile apps - Marketed as harmless entertainment options, these applications collect personal information under the pretense of gameplay, ultimately compromising privacy.
-
Disguised as legitimate banking applications, phishing mobile apps entice individuals into entering their login credentials, which are then captured for fraudulent purposes.
-
Social Media Impersonators
- These counterfeit versions of popular social media platforms are crafted to harvest individual information, potentially leading to identity theft and privacy violations.
-
Phishing mobile apps promise seamless email functionality, but instead, they serve as a front for stealing individuals' sensitive information, including passwords and personal identifiers.
-
Phishing mobile apps
- While claiming to enhance device performance, these fraudulent utility programs are actually designed to steal personal information, putting individuals at risk.
-
Advertised as solutions for enhancing online privacy, these applications often monitor user activity for harmful purposes, thus compromising the very security they claim to ensure.
-
Shopping Apps
-
Fraudulent e-commerce platforms that act as phishing mobile apps replicate legitimate retailers, aiming to capture credit card information and financial data from unsuspecting consumers.
-
Phishing mobile apps
-
These fraudulent security programs deceive individuals into believing they are safeguarded, while their actual intent is to jeopardize devices and gather sensitive data.
-
Impersonating Games
- By replicating popular gaming titles, these phishing mobile apps mislead users into disclosing personal data, posing a considerable threat in the mobile environment.
Awareness of phishing mobile apps is essential for protecting personal information and enhancing overall security.
With fraudulent email schemes remaining the leading method of cybercrime—an estimated 3.4 billion malicious emails sent daily—proactive measures are essential.
As noted by cybersecurity experts, 'Senior citizens were disproportionately targeted by vishing, with a 40% increase in attacks in the last two years,' highlighting the urgent need for vigilance across all demographics.
Moreover, the recent case study demonstrating how 'ChatGPT generated a deceptive login page in fewer than 10 queries' illustrates the evolving tactics in online scams, particularly with the use of AI.
Additionally, the FBI has issued warnings about fraud and deceptive schemes targeting borrowers related to the US Student Loan Forgiveness procedure, underlining the ongoing relevance and threat of such tactics in various sectors.
How Phishing Apps Operate: Techniques and Tactics
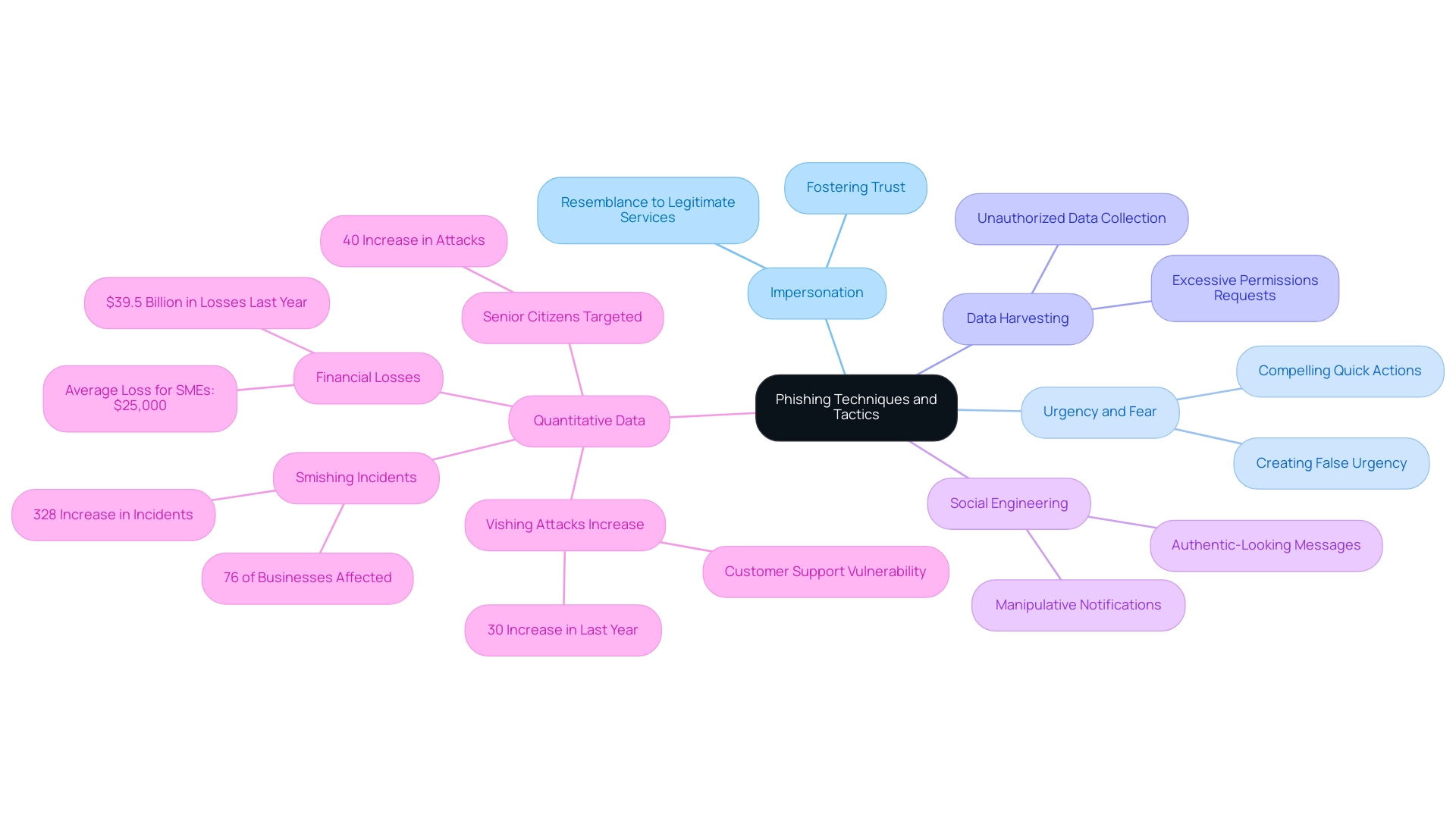
Phishing mobile apps employ a variety of advanced methods designed to mislead individuals and compromise their sensitive information. Key strategies include:
- Impersonation: Many fraudulent applications closely resemble legitimate services, fostering an immediate sense of trust among unsuspecting individuals.
- Urgency and Fear: These apps often create a false sense of urgency, compelling individuals to act swiftly without fully considering the implications of their actions.
- Data Harvesting: Once an individual is enticed into downloading a fraudulent application, it may request excessive permissions that facilitate unauthorized data collection, often without the individual’s awareness.
- Social Engineering: Phishing mobile apps use social engineering techniques to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information. This manipulation can take various forms, such as fake notifications or messages that appear authentic.
Recent data highlights a concerning trend: vishing attacks have surged by 30% over the past year, with customer support departments emerging as particularly vulnerable targets. Additionally, a staggering 76% of businesses reported experiencing smishing, leading to a 328% increase in incidents, underscoring the severity of the issue. Notably, senior citizens have been disproportionately affected, with a 40% rise in attacks over the last two years, resulting in significant financial losses that average $25,000 for small to medium-sized enterprises. This average loss indicates a wider trend, as phone scams resulted in an astonishing $39.5 billion in losses last year, highlighting the urgent necessity for users and organizations to comprehend these tactics, identify potential dangers, and implement proactive cybersecurity measures to protect against scams. As Lookout points out,
Mobile as a threat surface is poised to grow in the future.
This underscores the growing threat landscape and the importance of vigilance.
Protecting Yourself: Best Practices Against Mobile Phishing
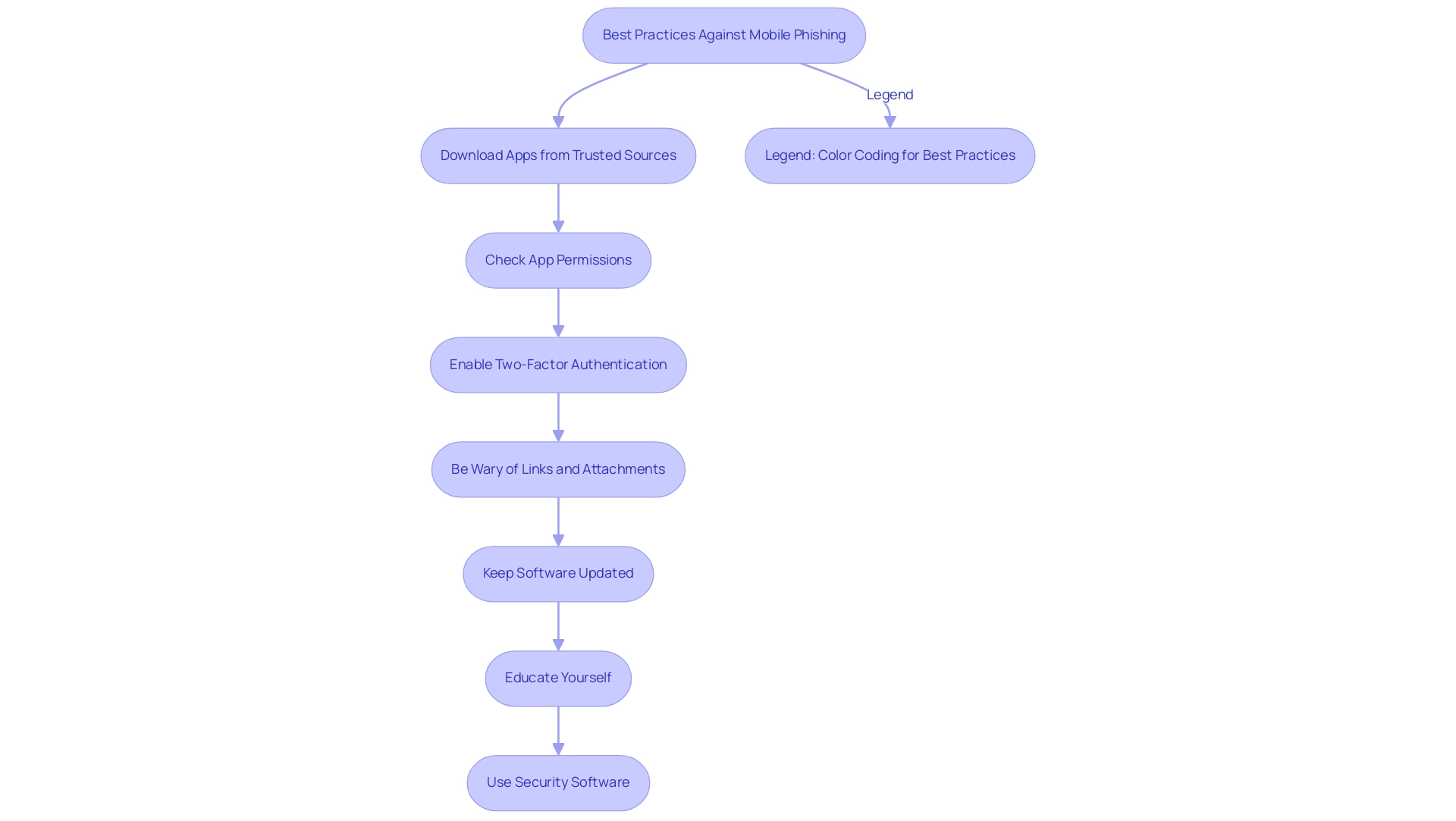
To effectively protect against phishing threats on devices, it is essential to adopt the following best practices:
-
Download Apps from Trusted Sources: Always install applications exclusively from official app stores, such as Google Play Store or Apple App Store. This significantly reduces the risk of downloading malicious software that could compromise your device.
-
Check App Permissions: Scrutinize the permissions requested by apps during installation. Deny access to unnecessary information that could expose your personal data, reinforcing your mobile security.
-
Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) on sensitive accounts for an added layer of protection. Research indicates that 2FA can reduce the risk of unauthorized access by up to 99%, making it a crucial defense mechanism against phishing.
-
Be Wary of Links and Attachments: Exercise caution when clicking on links or downloading attachments from unfamiliar sources. Cybercriminals often exploit these tactics to carry out deceptive attacks, making vigilance essential.
-
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your device’s operating system and applications to safeguard against known vulnerabilities. Outdated software can be an easy target for attackers, especially with recent vulnerabilities discovered in platforms like Chromium, which could enable attackers to execute heap corruption via malicious webpages.
-
Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest online scam tactics and trends. Ongoing education is essential in identifying potential threats, especially as deceptive techniques evolve. As noted by cybersecurity expert Milan Singh Thakur, understanding these tactics is a key element in defense strategies. Furthermore, the growing need for trained professionals in cybersecurity underscores the importance of education in combating such threats.
-
Use Security Software: Invest in reputable security software designed to enhance device protection against malware and fraudulent attempts. This software can provide real-time alerts and scans for suspicious activities, acting as an additional safeguard.
By implementing these best practices, users can significantly mitigate their risk of falling victim to phishing attacks, promoting a safer environment. Additionally, it's crucial to recognize that 31% of CISOs report projects being delayed or removed due to lack of funding, highlighting the importance of investing in mobile security measures to protect against evolving threats.
Conclusion
Mobile phishing represents a significant and growing threat in today's digital landscape, as cybercriminals increasingly exploit the very applications that users rely on daily. By understanding the tactics employed by these malicious actors—such as impersonation, urgency, and data harvesting—individuals and organizations can better equip themselves to recognize and counteract these risks. The prevalence of phishing apps, including those masquerading as banking services, social media platforms, and even utility applications, underscores the urgent need for vigilance.
To effectively combat mobile phishing, implementing best practices is essential. The following steps are critical in creating a robust defense:
- Download apps only from trusted sources.
- Scrutinize app permissions.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Remain cautious about unfamiliar links and attachments.
Additionally, staying informed about the latest phishing trends and investing in reputable security software can further enhance protection against these evolving threats.
In conclusion, as the tactics of cybercriminals continue to advance, proactive measures and continuous education are imperative. By fostering awareness and adopting comprehensive security practices, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to mobile phishing, ultimately safeguarding their personal and organizational data in an increasingly perilous digital environment.





