Introduction
The concept of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) has become increasingly important in the e-commerce industry. An MVP is a streamlined version of a product that allows businesses to test their ideas, gain user feedback, and validate market demand with minimal effort and cost. It serves as a learning tool and a stepping stone to success, enabling businesses to refine their products based on real-world testing and insights. In this article, we will explore the significance of MVPs in e-commerce, the core components of an e-commerce MVP, the cost factors involved in building an MVP, the role of market research in cost estimation, and the importance of balancing quality and cost-effectiveness in MVP development. We will also examine real-life case studies of successful implementation of e-commerce MVPs, showcasing the effectiveness of this approach in driving growth and success in the industry. Whether you're a startup or an established business, understanding and leveraging the power of MVPs can help you create a successful e-commerce platform that meets the needs and preferences of your target audience.
1. Understanding the Concept of MVP in E-commerce
The concept of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) plays a pivotal role in the digital commerce sector. It refers to a pared-down version of a new product, designed to garner the maximum amount of validated customer insights with the least amount of effort. This strategy is leveraged for swift, quantitative market testing of a product or its features. An MVP is that version of the product that enables a complete cycle of the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop with minimal effort and the shortest development time. This strategy expedites the learning process for business owners since it is the fastest route through the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop with minimal effort.
Indie Hackers, a community platform for founders and creators, underscores the importance of MVPs for startups. The platform allows users to explore and discover indie hacker products, engage with podcasts and meetups, and even purchase Indie Hackers merchandise. One of the key topics discussed on the platform is the significance of MVPs for startups. The platform's discussion debunks several common misconceptions about MVPs, such as the belief that an MVP is merely a smaller version of the final product or that it should possess more features than its competitors. Instead, the discussion highlighted that an MVP is more than just a product—it's a learning tool and a process.
Several renowned companies, including Dropbox, Uber, Airbnb, Spotify, Twitter, and Product Hunt, began their journeys as MVPs and later found success. For instance, Dropbox began with a simple MVP that focused on file synchronization. They made a three-minute video demonstrating their service, which attracted thousands of users practically overnight. Uber, on the other hand, started as an MVP called UberCab, which aimed to connect users with cab drivers and facilitate in-app payments. Based on user feedback, they gradually expanded the application's functionality.
Airbnb is another fascinating MVP success story. The founders began by renting out air mattresses in their apartment during a conference. Once they validated their idea, they began redesigning and expanding the platform. Spotify, now a global music streaming giant, began as an MVP that allowed users to legally and instantly stream music for a small fee. As the platform gained popularity, they gradually added more features and signed more artists.
Zappos, now a billion-dollar online shoe retailer, began as an MVP where the founder tested the hypothesis that people would be willing to buy shoes online. He photographed shoes from local stores and uploaded the pictures to a simple website to validate the idea. Buffer, a social media management platform, also began as an MVP landing page. The founder created a two-page website to test whether people would be interested in a software product that scheduled tweets. Once he received positive feedback and interest, he built the actual product.
Twitter, now a billion-dollar social network, started as an internal tool called Twttr, used by employees of podcasting company Odeo for posting status updates via SMS. As it gained acceptance, it was launched for a larger market. Product Hunt, a platform for discovering new products, started as an email list. Upon receiving positive feedback, the founder created a wireframe and gathered feedback from fifty individuals in the technology sector. This eventually evolved into a platform with a million users.
These examples clearly demonstrate the benefits of building an MVP to validate market demand and avoid costly mistakes. The MVP approach allows businesses to save time and resources and validate market demand. The journey of these successful companies underscores the value and potential of starting with a Minimum Viable Product. It's not just a product—it's a process, a learning tool, and a stepping stone to success.
When it comes to building an e-commerce MVP, it is crucial to follow a systematic approach. Begin by identifying the core features that are essential for your e-commerce product. These features typically include product listing, shopping cart functionality, payment gateway integration, and user authentication. Prioritize these features based on their importance and feasibility. Focus on the most critical features that provide value to your users and can be developed within a reasonable timeframe. This will help you launch the MVP quickly and gather user feedback.
Once you have defined the core features, start designing the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of your e-commerce product. Ensure that the design is intuitive, visually appealing, and aligns with your target audience's preferences. After designing, you can proceed with the development phase. Depending on your resources and expertise, you can choose to develop the MVP in-house or outsource it to a development team. It is advisable to leverage existing e-commerce platforms or frameworks to speed up the development process.
During the development phase, focus on building the core features first and keep the development cycle short. This iterative approach allows you to test and validate your assumptions early on and make necessary improvements based on user feedback. Once the MVP is developed, conduct thorough testing to identify and fix any bugs or issues. It is crucial to ensure that the e-commerce product functions smoothly and provides a seamless user experience. Lastly, launch the MVP and monitor user behavior and feedback closely. Analyze user data and iterate on the product based on the insights gained. This continuous improvement process will help you refine the e-commerce product and align it with market demands.
Remember, building an MVP is an iterative process, and it is important to remain agile and adaptable to changes based on user feedback and market trends.
2. The Core Components of an E-commerce MVP
An effective e-commerce Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is defined by its core components, each serving a unique purpose and contributing to the overall user experience. These components not only define the functionality of the platform, but also its value proposition, enabling a seamless shopping journey for the users.
In the context of an e-commerce MVP, a critical component is its user-friendly interface. This interface should be designed to facilitate easy navigation and interaction for users, enhancing their overall shopping experience. Best practices in designing such an interface include simplifying navigation, having a clear product display, streamlining the checkout process, ensuring mobile responsiveness, implementing effective search functionality, using clear calls to action, minimizing distractions, and providing user-friendly feedback and error handling.
Another vital component of an e-commerce MVP is a secure payment gateway. An e-commerce platform must ensure the protection of user financial information during transactions to build trust and confidence. Various secure payment gateway options available in the market offer encryption and other security measures to safeguard sensitive data.
The product catalog, another crucial feature of an e-commerce MVP, should be methodically organized, displaying a broad range of products with high-quality images and detailed product descriptions. To create an appealing product catalog, it is essential to logically categorize products, use high-quality product images, and provide clear and concise product descriptions.
Customer reviews significantly contribute to the platform's credibility. They provide valuable insights into the experiences of previous customers, helping potential customers make informed purchasing decisions. To encourage and manage customer reviews, it is important to create a user-friendly interface, incentivize customers to leave reviews, and actively manage customer feedback.
The search and navigation feature, allowing users to quickly locate specific products or categories, is a fundamental part of an e-commerce MVP. Best practices for implementing this feature include ensuring that the search function is user-friendly and provides relevant results, having a clear and intuitive menu structure, incorporating filters and sorting options, and including a prominent search bar and navigation menu in a consistent and easily accessible location on every page of the website.
BigCommerce exemplifies the successful implementation of these core components. As an enterprise e-commerce platform catering to various industries, its comprehensive set of features, including data personalization, solutions for large catalog management, multi-currency, omnichannel management, payment solutions, SEO, site optimization, and social media advertising, contribute to a seamless consumer experience.
Similarly, a fashion aggregator developed an MVP for a fashion marketplace, incorporating services including design, backend development, frontend development, architecture, and product development. The platform's success, demonstrated by its ability to raise $500k and attract 11k visitors a month, highlights the effectiveness of these core components in driving the success of an e-commerce platform.
Thus, the core components of an e-commerce MVP play a pivotal role in its success. They enhance the user experience, build trust and credibility, facilitate easy navigation and search, ensure secure transactions, and showcase a wide range of products. These features are critical in ensuring the functionality and value of the platform, driving its success and growth in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
3. Determining the Cost Factors for Building an MVP
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) requires a strategic approach that involves numerous considerations, with cost being a key factor. The financial commitment necessary for the development of an MVP can be influenced by a host of elements. These include the complexity of the product, the number of features, the technology employed, and the geographical location of the development team.
The cost of MVP development is not merely a reflection of the product's complexity or the number of features. Rather, it is also influenced by the level of customization required, the technology stack chosen, and the expertise and experience of the development team. The development timeline can also have a significant impact on the cost. For a more accurate estimation and management of the cost of building an MVP, it's crucial to work closely with the development team and thoroughly consider these factors.
The MVP development process includes several stages: discovery, prototyping and design, app development, quality assurance, and optimization.
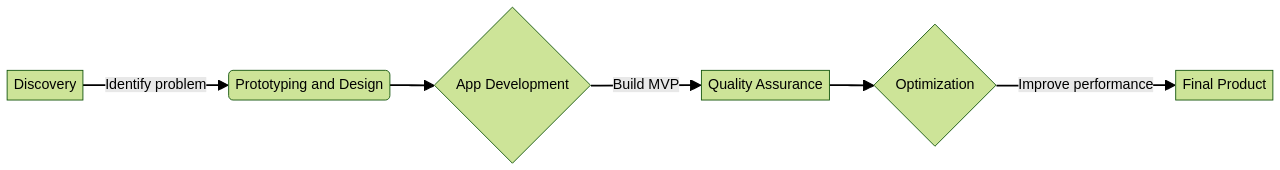
Each of these stages comes with its own set of costs, and the overall cost can range from $24,000 to $96,000 on average. The time to market is typically 4-5 months.
The benefits of MVP development are manifold, including risk reduction, quicker time to market, cost-effectiveness, a user-centric approach, and the ability for iterative improvements. Successful companies like Twitter, Uber, and Dropbox began their journey with simple MVPs that evolved over time into market-leading solutions.
When planning for MVP development, it's advisable to prioritize essential features, choose between in-house and outsourced development teams, analyze hourly rates, consider geographical location, and assess contract types. After the launch, additional costs might come into play, such as marketing and promotion, maintenance, and sustaining the MVP.
To mitigate the cost of building an MVP, you can resort to consulting services. These services provide access to top-tier talent, including software developers, designers, and QA specialists. They offer flexible, on-demand solutions that can integrate into an existing team or work as separate contractors to expedite development and align with market demands. Whether for a quick proof of concept, initial project research, bug fixes, or full outsourcing, consulting services can provide cost-effective and flexible solutions.
In sum, the cost of MVP development can be influenced by a wide range of factors. It's essential to remember that the primary objective of an MVP is not merely to create a scaled-down version of the final product but to gain insights into the customers' needs and preferences. MVP development allows startup owners to test their ideas, gain feedback, and adapt their solutions to meet user needs.
4. The Role of Market Research in Cost Estimation
A critical step in the journey of creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is understanding the market which is instrumental in estimating the associated expenses.
This comprehension not only entails gaining insights into potential customers and their preferences but also recognizing current market trends. This knowledge aids in determining the essential features for the MVP, a decision that has a direct impact on the overall cost. Conducting market research can shed light on the competitive landscape and competitors' offerings, guiding the pricing strategy.
The MVP development process is a strategic approach to introducing a new product to the market. It commences with a basic version of the product that incorporates the essential features. This methodology facilitates the testing of the product concept and the collection of customer feedback. The costs linked with MVP development can vary extensively, influenced by several factors including the project's scope, team selection, hourly rates, the team's location, the developers' qualifications, and the type of contract.
The MVP development process encompasses several stages, including the discovery phase, prototyping and design, app development, quality assurance, and optimization.
On average, the cost of developing an MVP ranges from $24,000 to $96,000, with a typical time to market of 4 to 5 months. Utilizing the MVP approach provides numerous benefits such as risk mitigation, faster time to market, cost-efficiency, user-centric design, and the opportunity for iterative improvement.
Several successful companies, such as Twitter, Uber, and Dropbox, initiated with simple MVPs and refined their concepts based on user feedback.
Various factors can impact the cost of MVP development, including the core functionality, user interface design, content or data volume, feedback collection methods, and performance and stability optimization.
To mitigate the cost of MVP development, it might be beneficial to prioritize essential features, consider outsourcing development teams, analyze hourly rates, consider location, and choose the appropriate contract type. Post-launch, additional costs to consider include marketing and promotion, MVP maintenance, and ongoing data analysis and optimization.
Hiring an MVP development firm can aid startups in conserving time and resources that would otherwise be spent on locating and managing development teams. On average, the cost of an MVP is around $76,325, and the average time to develop an MVP is 4-5 months.
The success of Twitter, Uber, and Dropbox serves as a testament to the effectiveness of starting with a simplified version of a product and gathering user feedback to refine the final product. These cases demonstrate how MVPs can lead to success and the refinement of the final product.
Reinforcing the significance of market research, the team of software developers, designers, and engineers at BestToolbars.net offers market analysis and cost estimation for your MVP. They provide consulting services to assist you in launching your MVP, testing its market fit, and accessing top-tier talent. The specialists at BestToolbars.net work with you on testing market hypotheses, conducting initial project research, and aligning your product with the market. They offer a range of services, whether you need a quick proof of concept, bug fixes, or full outsourcing.
5. Balancing Quality and Cost-effectiveness in MVP Development
Creating a cost-effective Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that does not compromise on quality is a pivotal step in the product development process. The MVP is a streamlined version of a product that possesses just enough features to satisfy initial customers and provide feedback for future enhancements. It forms a scalable foundation for future product improvements.
Building an MVP is cost-effective, but it's paramount to ensure the quality of the product is maintained.
Ensure quality while building a cost-effective MVP
An inferior MVP can lead to unfavorable user experiences and impact the product's overall perception negatively. Thus, it's crucial to strike a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality during MVP development.
To achieve this balance, businesses can concentrate on the most vital features that deliver value to the customers. This approach allows businesses to validate their product's functionality and identify what functionalities need to be added or modified. It ensures the MVP is a comprehensive and usable software that allows businesses to test, gain user insights, and continuously improve development based on real-world testing and feedback.
Another key aspect of MVP development is investing in good design and user experience. While an MVP doesn't need to have a fancy design, the User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) should be intuitive and straightforward. This is because the primary purpose of an MVP is to test the product's essence and analyze user feedback, which can only be achieved if the product's design is user-friendly.
Building an MVP can be up to four times faster and one quarter cheaper than a full product.
Build your MVP quickly and cost-effectively
This speed and cost-effectiveness, combined with the opportunity for more testing time and tangible feedback from users, make MVP development an attractive option for startups and small businesses.
Prominent companies like Spotify and Airbnb began with MVPs, demonstrating the effectiveness of this approach. Spotify started as a small service with just one function - music streaming. Today, it has a market valuation of 50 billion, partnerships with major recording studios, and a 50 million active audience. Airbnb, on the other hand, started by renting out their own apartment by fax, which served as an MVP to test the demand for their idea. Today, Airbnb is one of the largest sites for finding short-term rental housing.
While striving for cost-effectiveness in MVP development, it's crucial not to compromise on quality. Focusing on the most important features and investing in good design and user experience can help achieve this balance. The success stories of companies like Spotify and Airbnb underline the potential of well-developed MVPs in quickly establishing market fit and attracting potential investors.
6. Case Study: Successful Implementation of an E-commerce MVP
The concept of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) has played a pivotal role in the success stories of many e-commerce platforms. A significant example of this approach is Joydrive, an online platform that has revolutionized the car purchasing process. The founder, Hunter Gorham, collaborated with Thoughtbot, a strategic technical partner, to bring this innovative product idea to fruition.
Thoughtbot, acting as Joydrive's CTO partner, conducted a product design sprint to validate the business model. This comprehensive approach included extensive research, expert interviews, and the development of an MVP within a tight six-week timeframe. This swift deployment allowed Joydrive to validate their business model without a substantial upfront investment.
The MVP provided an opportunity to gain insights into their roadmap and tailor their product based on real user needs. This approach proved successful, with customers making active car purchases through the application, signaling Joydrive's readiness to scale.
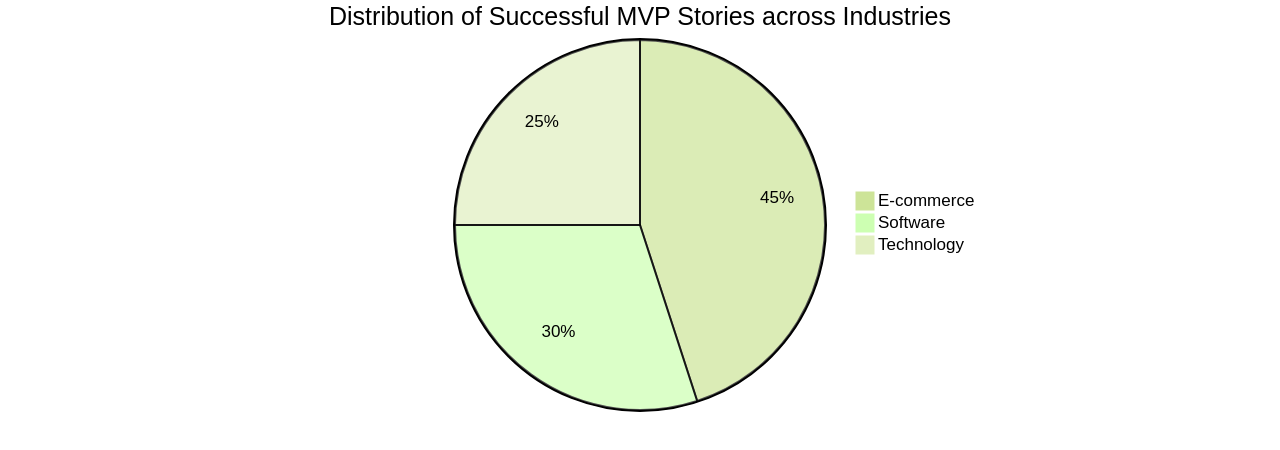
Another instance of the MVP approach's success in e-commerce is Octane AI, a provider of AI-powered tools for businesses. They developed a unique AI-powered quiz maker to gather customer insights, personalize marketing efforts, and boost conversion rates. Mavi, a brand that leveraged Octane AI's shop quiz and messenger marketing solutions, experienced an impressive 12x ROI, underscoring the MVPs' power in validating business models and strategies.
The MVP approach's effectiveness is not limited to these examples. Shopify, Etsy, and Amazon are renowned e-commerce platforms that started as MVPs. Shopify's initial simplicity, Etsy's focus on a niche market, and Amazon's vast book selection all served as MVPs that evolved into leading platforms in the e-commerce industry.
BestToolbars.net is another resource for understanding the MVP approach's success. Their innovative solutions and consulting services assist in launching MVP products and testing market fit. They offer full outsourcing options, which can expedite development, test hypotheses, and align products with the market.
Zappos, known for its exceptional customer service and seamless online shopping experience, also validated its business idea with an MVP. Their approach to market fit testing and gathering user feedback allowed them to align their product with the market, ensuring the viability of their business idea before scaling up.
Building an MVP in the e-commerce industry involves adhering to certain best practices. Foremost among these is focusing on the product's core functionality and prioritizing features that provide value to users. This allows for a quick product launch and market fit testing. Incorporating a team of software developers, designers, and QA specialists can accelerate the development process and ensure the product aligns with market needs. Initial project research, hypotheses testing, and bug fixing are also crucial steps for market alignment.
The MVP approach's success stories underscore the importance of validating business ideas through MVPs, leading to significant growth and success in the e-commerce industry.
Validate your business idea with an MVP
By starting with a minimum viable product and iterating based on user feedback, companies can build scalable and successful e-commerce platforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is an essential strategy in the e-commerce industry. An MVP allows businesses to test their product ideas, gather user feedback, and validate market demand with minimal effort and cost. It serves as a learning tool and a stepping stone to success, enabling businesses to refine their products based on real-world testing and insights. The examples of successful companies like Dropbox, Uber, Airbnb, Spotify, Twitter, and Product Hunt demonstrate the effectiveness of building an MVP to validate market demand and avoid costly mistakes. By understanding the significance of MVPs in e-commerce and implementing this approach, businesses can create successful platforms that meet the needs and preferences of their target audience.
The core components of an e-commerce MVP are crucial for its success. These components include a user-friendly interface, a secure payment gateway, a well-organized product catalog, customer reviews, and effective search and navigation features. By focusing on these components and ensuring their quality, businesses can provide a seamless shopping experience for users and build trust and credibility in their platforms.
To build an MVP in a cost-effective manner, it is important to consider factors such as the complexity of the product, the number of features, the technology employed, and the geographical location of the development team. Conducting market research plays a significant role in estimating costs accurately by understanding potential customers' preferences and current market trends. Balancing quality and cost-effectiveness is crucial during MVP development to ensure that the product meets user expectations while being efficient in terms of resources. By following these principles and leveraging consulting services when needed, businesses can navigate the e-commerce landscape successfully.
Start now to leverage the power of MVPs in your e-commerce journey.





