Introduction
Embedded software plays a vital role in driving solutions and innovation across various sectors. With its deep integration into hardware systems, embedded software companies have been instrumental in enhancing business operations and enriching consumer experiences in fields like automotive and healthcare.
In this article, we will explore the pivotal role of embedded software, successful case studies, benefits for businesses, challenges faced in development, and best practices for effective implementation. By delving into these aspects, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic landscape of embedded software and its impact on the evolving technological terrain.
The Role of Embedded Software in Driving Solutions
At the heart of innovation across numerous sectors, embedded software companies have been pivotal in crafting progressive solutions that align with the intricate demands of fields like automotive and healthcare. It's this deep integration of software within hardware systems that facilitates the smooth function of devices, catalyzing enhanced business operations and enriched consumer experiences.
Chief Scientist Arpan Pal elucidates this by underlining the essence of hardware-software co-design in embedded systems. This synergy articulates both the hardware's capacity and the software's unique attributes, laying the groundwork for advancements such as Embedded Edge Computing, which is burgeoning to augment AI in embedded systems.
Notably, initiatives like Switzerland's new legal frameworks seek to buttress digital sovereignty, underscoring the imperative need for such embedded software innovations. Pal advises that the secret to excelling in embedded systems is to be agile with technology adaptation, citing the unpredictable evolution of AI within embedded contexts. His guidance offers a strategic perspective: to methodically focus on the problem at hand and harness technology as a solution rather than the converse. This mindset positions embedded software companies to continuously pioneer within the nexus of technology and practical applications, thereby unfolding unprecedented opportunities for growth and evolution in the dynamic landscape of embedded systems.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Embedded Software Solutions
Embedded software companies like XYZ Technologies are revolutionizing safety with their cutting-edge algorithms in driver assistance systems. In a noteworthy partnership with a premier automotive manufacturer, XYZ Technologies harnessed the power of embedded software to bolster driver safety.
The project undertook the challenge of formulating algorithms capable of perceiving and aptly reacting to on-road hazards. The result was a marked decrease in vehicular accidents, showcasing the pivotal role embedded systems play in enhancing road safety.
Renowned Chief Scientist Arpan Pal emphasizes the importance of synergy between hardware capabilities and software innovation in such projects. According to Pal, the hardware-software co-design is crucial in developing responsive and reliable embedded systems. Moreover, he advises openness and adaptability to burgeoning technologies, exemplified by the emergence of Embedded Edge Computing in integrating Artificial Intelligence with embedded systems. Tapping into this potential, XYZ Technologies demonstrated the practical application of such advice by focusing on a real-world problem—road safety—and deploying technology as a solution, rather than gambling on unproven technology in search of an application.
Benefits of Embedded Software Development for Businesses
Embedded software development is transforming businesses by enabling smart, connected devices that not only enhance functionality but also significantly elevate user experiences. These devices become an integral part of our modern ecosystem, embedded in everything from household appliances to sophisticated medical apparatuses, and go beyond mere convenience—they become essential to operational efficiency.
With dedicated functionality, embedded systems are meticulously engineered to handle specific tasks, such as regulating a vehicle's engine performance or monitoring patients' health statuses in real-time. By focusing on specialized applications, companies can tailor experiences and functionality precisely to user needs, which, in turn, drive up the value proposition.
However, resource constraints in such embedded systems necessitate ingenious approaches to maximize efficiency. This often means streamlining operations is not just a benefit but a necessity that embedded software deftly addresses.
Through this optimization, businesses observe a palpable reduction in costs and improvements in overall efficiency. Security, distinct yet equally important as safety, becomes a paramount consideration in this field.
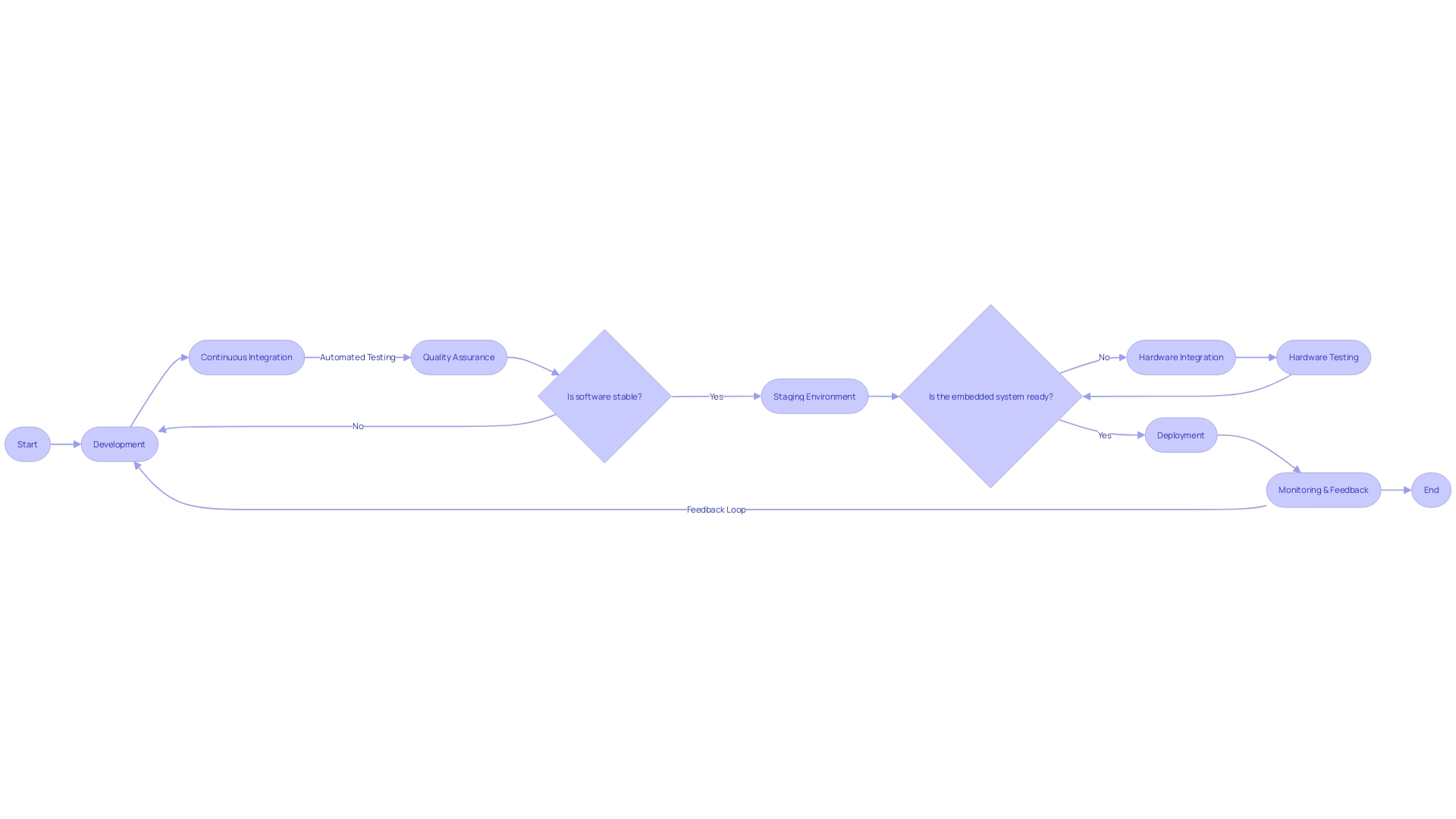
It's a diurnal struggle to defend these systems from intentional threats and malicious actions. Continuous Delivery (CD) plays a vital role in this domain, providing a means to release software updates with both greater speed and reliability. CD signifies not just a set of tools but also a paradigm shift—embracing a culture of co-shared responsibility for software reliability across the organization. Nevertheless, we recognize the software landscape is fraught with risks, hinted at by experts emphasizing the dire state of software security and the often precarious balance between embracing rapid innovation and upholding stringent security standards. In conclusion, embedded software is leading a revolution that reshapes businesses and consumer interactions. Its integration into devices bolsters better performance, enhanced user experience, and a more secure and efficient operational framework, fostering an environment of innovation that's critical in today's rapidly evolving technological terrain.
Challenges and Opportunities in Embedded Software Development
Embarking on embedded software development is akin to navigating a labyrinth where each turn presents unique challenges and possibilities. The core of the endeavor is the intricate task of marrying software with hardware—an endeavor that demands not only technical prowess but also a holistic understanding of both realms.
As embedded systems serve as the brains within a myriad of devices from household appliances to life-saving medical equipment, they have to operate with precise dedication and within the bounds of their resources; think of a system simultaneously as compact as a pacemaker yet as complex as an autonomous vehicle's control system. Even as developers push the boundaries of what's possible, optimizing software for peak performance is an ever-evolving marathon.
It's a high-stakes arena where balancing functionality, safety, and security is paramount, especially given the explosive growth of the IoT market, which is transforming everything from home automation to global communication networks. As Industry pundits have noted, time is of the essence, and simulation tools may just be the linchpin in accelerating the time to market while judiciously managing development costs. This confluence of relentless innovation and strategic efficiency is where embedded software companies strive to distinguish themselves—and lead the charge in an increasingly connected world.
Best Practices for Effective Embedded Software Development
Embedded software development, a field intertwined with hardware design, has evolved to embrace Continuous Delivery (CD)--an approach where teams release incremental updates rapidly, reliably, and safely. Compared to traditional methods that keep software and hardware phases distinct, CD integrates them closely, resulting in quicker, more reliable deployment and testing cycles, aligning with the agile ethos. Toyota's Woven Planet's troubles exemplify the importance of matching grand visions with practical execution.
The unit, designed to create cross-compatible automotive software, faltered due to over-ambition and misaligned schedules, proving innovative software development requires flexible timelines and a careful balance of expectations. To achieve the 'holy grail' of faster market entry and lower costs, developers require not just tools but a mindset and cultural shift, emphasizing shared responsibility for software across all development stages. Simulation has been touted as a pathway to these goals, with claims that it facilitates quicker, cost-effective development—principles at the core of continuous delivery's promise.
Conclusion
Embedded software plays a pivotal role in driving solutions and innovation across various sectors. By integrating software within hardware systems, embedded software companies enhance business operations and enrich consumer experiences.
Successful case studies, like XYZ Technologies' implementation of embedded software in driver assistance systems, showcase the importance of synergy and adaptable technology adoption. Embedded software development brings benefits for businesses by transforming smart, connected devices that enhance functionality and elevate user experiences.
Tailored embedded systems increase operational efficiency and reduce costs while addressing resource constraints. Security and safety are crucial considerations, with Continuous Delivery (CD) ensuring reliable software updates.
The challenges in embedded software development include marrying software with hardware and balancing functionality, safety, and security in the rapidly evolving IoT market. However, by adopting best practices, such as embracing Continuous Delivery, companies can navigate these challenges and unlock opportunities for growth. In conclusion, embedded software revolutionizes businesses and consumer interactions. It enhances performance, user experience, and security while fostering innovation. By staying ahead of the dynamic landscape, embedded software companies can drive impactful solutions and shape the future of technology.





