Introduction
In an age where patient privacy is paramount, understanding the intricacies of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential for any organization handling sensitive health information. HIPAA not only establishes stringent standards for the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI) but also serves as a critical framework for fostering trust between healthcare providers and patients.
With the growing prevalence of data breaches and the severe penalties associated with non-compliance, organizations must prioritize their adherence to these regulations. This article delves into the fundamental principles of HIPAA, outlines key compliance rules for web applications, and offers a step-by-step guide to achieving compliance, ensuring that healthcare entities are equipped to safeguard patient data effectively.
Understanding HIPAA: Importance and Overview
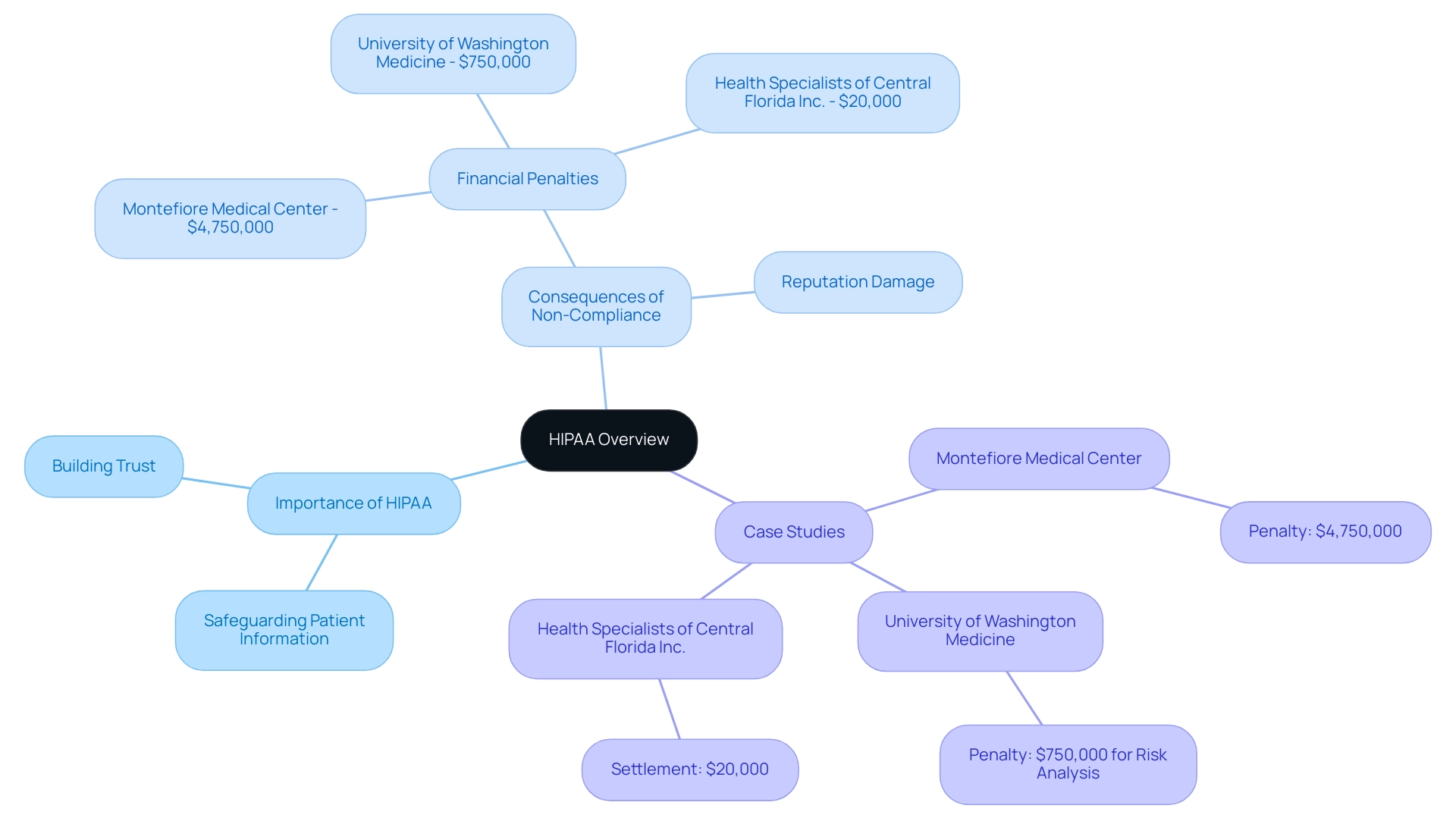
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act functions as a cornerstone in safeguarding sensitive patient information, ensuring that electronic protected health information (ePHI) is not disclosed without the patient's consent. This legislation establishes rigorous standards for information security across various sectors, most notably in healthcare. Adherence to healthcare regulations is not simply a legal obligation; it is also an essential part of building trust between healthcare organizations and their patients.
Non-compliance can lead to severe repercussions, including substantial fines and damage to an organization's reputation. For instance, Montefiore Medical Center faced a staggering penalty of $4,750,000 due to a data breach, highlighting the financial stakes involved. Additionally, the yearly sums of healthcare privacy violation penalties from 2008 to H1 2024 demonstrate a troubling trend in financial consequences for non-compliance.
In a recent example, the University of Washington Medicine was fined $750,000 for failing to conduct an organization-wide risk analysis, underscoring the real-world implications of privacy law violations. Furthermore, as Jocelyn Samuels, Director of OCR, stated,
While OCR prefers to resolve issues through voluntary compliance, we will take the steps necessary, including litigation, to obtain adequate remedies for violations of the health information privacy regulations.
Another case study involving Health Specialists of Central Florida Inc. resulted in a $20,000 settlement to resolve a Right of Access investigation, illustrating the potential for financial settlements in violation cases.
Grasping the basic concepts of HIPAA compliance for web applications is vital for any application that handles or retains electronic protected health information, as it not only safeguards patient information but also strengthens the trust that is critical in the healthcare environment.
Key HIPAA Compliance Rules for Web Applications
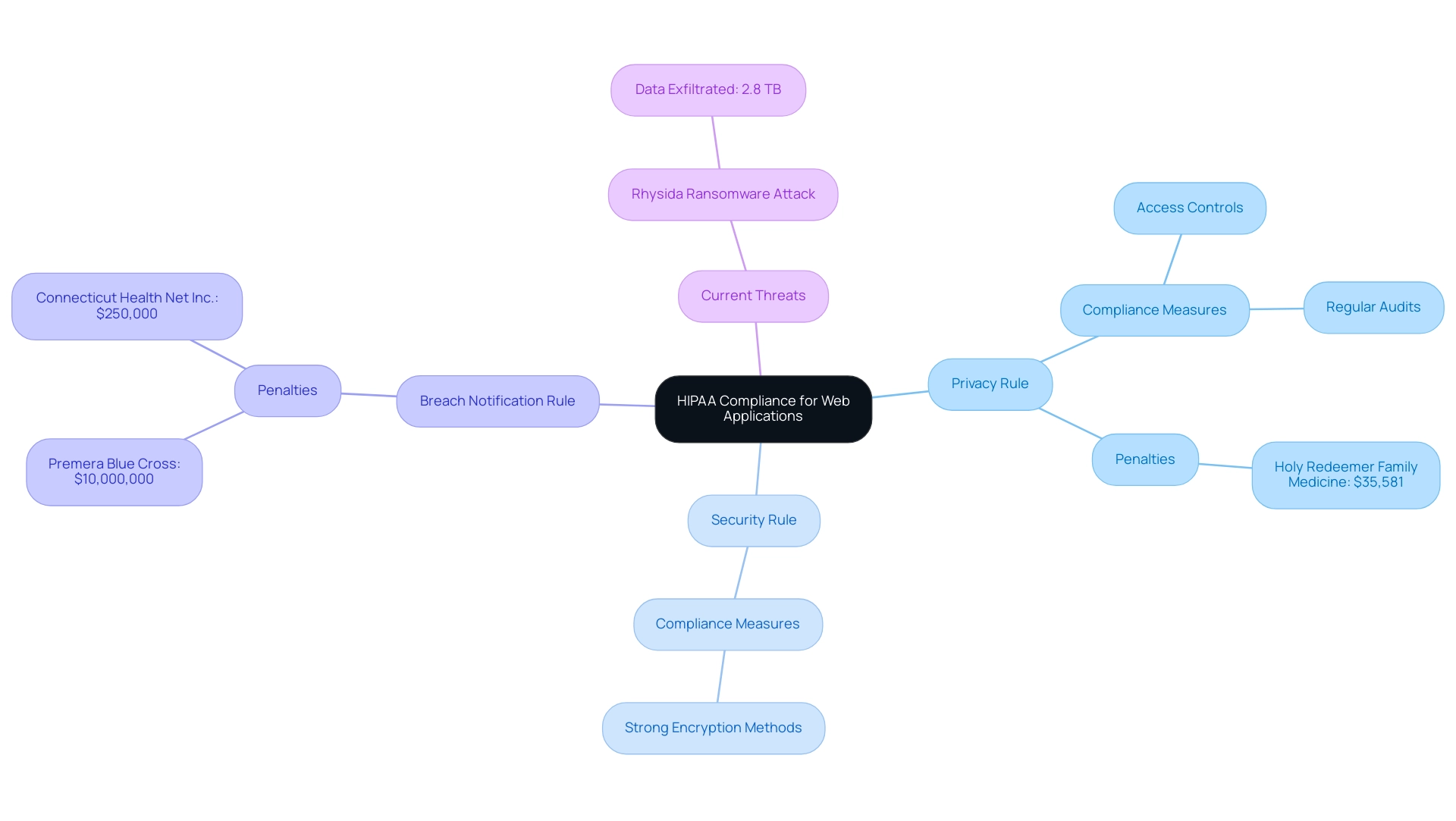
Achieving HIPAA compliance for web applications is anchored in understanding several pivotal regulations, primarily the Privacy Rule, which dictates the permissible use and disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI). Alongside this, the Security Rule establishes rigorous standards for the protection of electronic PHI (ePHI), while the Breach Notification Rule mandates timely notification to affected individuals in the event of a security breach. To ensure HIPAA compliance for web applications, it is essential to adopt comprehensive safeguards across three domains: administrative, physical, and technical.
This includes:
- Implementing robust access controls
- Employing strong encryption methods
- Conducting regular audits to identify vulnerabilities
The case of Holy Redeemer Family Medicine underscores the importance of these measures; following an impermissible disclosure of a patient's reproductive health information, the facility incurred a penalty of $35,581 due to a violation of the HIPAA Privacy Rule. Additionally, the financial repercussions of non-compliance are starkly illustrated by the case of Connecticut Health Net Inc., which was fined $250,000.
This highlights the significant risks organizations face. Additionally, as Steve Alder highlighted, 'There is presently no breach report on the American Addiction Centers website; however, the Rhysida ransomware group took responsibility for the attack and stated 2.8 TB of information was exfiltrated, 90% of which has been uploaded to its leak site.' Such current threats highlight the necessity for strong adherence measures.
Moreover, Premera Blue Cross encountered a staggering $10,000,000 penalty in a multistate action in 2019, reinforcing the critical need for organizations to prioritize HIPAA compliance for web applications, not only to protect patient data but also to mitigate significant legal and financial repercussions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Achieving HIPAA Compliance
-
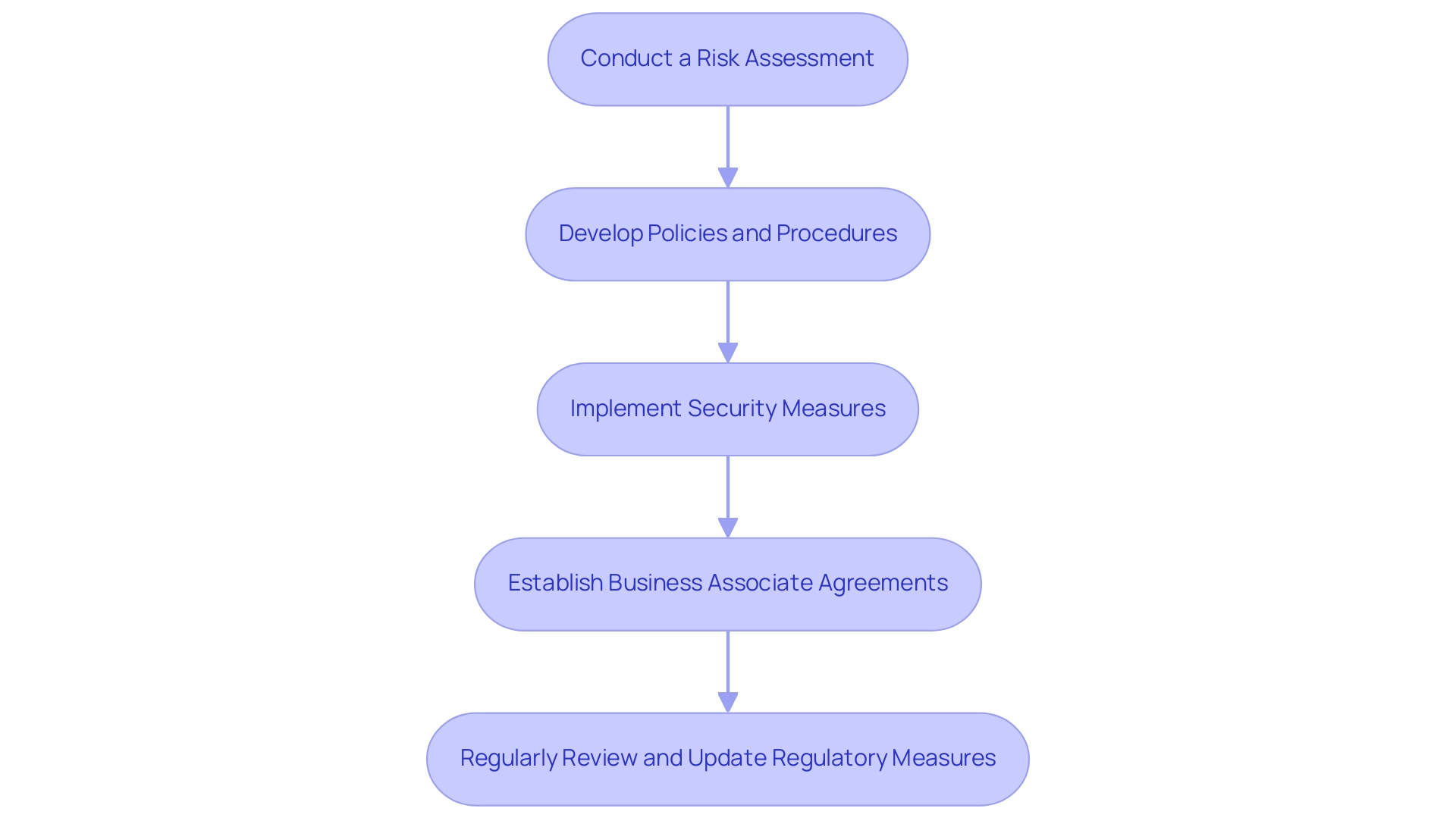
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Start by identifying potential risks to electronic Protected Health Information to ensure HIPAA compliance for web applications. This foundational assessment serves as a crucial roadmap for your regulatory strategy, allowing you to pinpoint vulnerabilities that could lead to breaches. As noted, it is important for organizations to monitor changes to transaction code systems for two reasons.
-
Develop Policies and Procedures: Formulate comprehensive policies that govern the use and safeguarding of ePHI. It's essential that all team members undergo training to ensure they understand and adhere to these policies, fostering a culture of compliance within your organization. Reference the three main rules of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act: the Privacy Rule, Security Rule, and Breach Notification Rule, as they provide a clear framework for your policies.
-
Implement Security Measures: Deploy necessary technical safeguards, including encryption, robust access controls, and secure data storage solutions. These measures are essential in safeguarding electronic protected health information from unauthorized access and ensuring HIPAA compliance for web applications in accordance with the HIPAA Security Rule.
-
Establish Business Associate Agreements (BaaS): If your web application collaborates with third-party vendors, ensure that you have BaaS in place. These agreements are critical for delineating the responsibilities of all parties involved in handling ePHI, thus safeguarding sensitive information.
-
Regularly Review and Update Regulatory Measures: Acknowledge that adherence is an ongoing process. Regularly evaluate your practices and update them as necessary to ensure HIPAA compliance for web applications while adapting to evolving regulations, such as the ongoing lawsuit by the Texas Attorney General challenging the legality of updates to the HIPAA Privacy Rule regarding reproductive health information. Staying proactive in your regulatory efforts not only mitigates risks but also aligns your organization with best practices in the industry.
A well-organized documentation system is essential for readiness, ensuring you have records of staff training, BaaS, and breach notification protocols readily available during audits. As mentioned, organizations can appoint a privacy expert to manage privacy-related matters and offer yearly training for employees, emphasizing the significance of ongoing education in ensuring adherence.
Technical Safeguards and Security Measures for Compliance
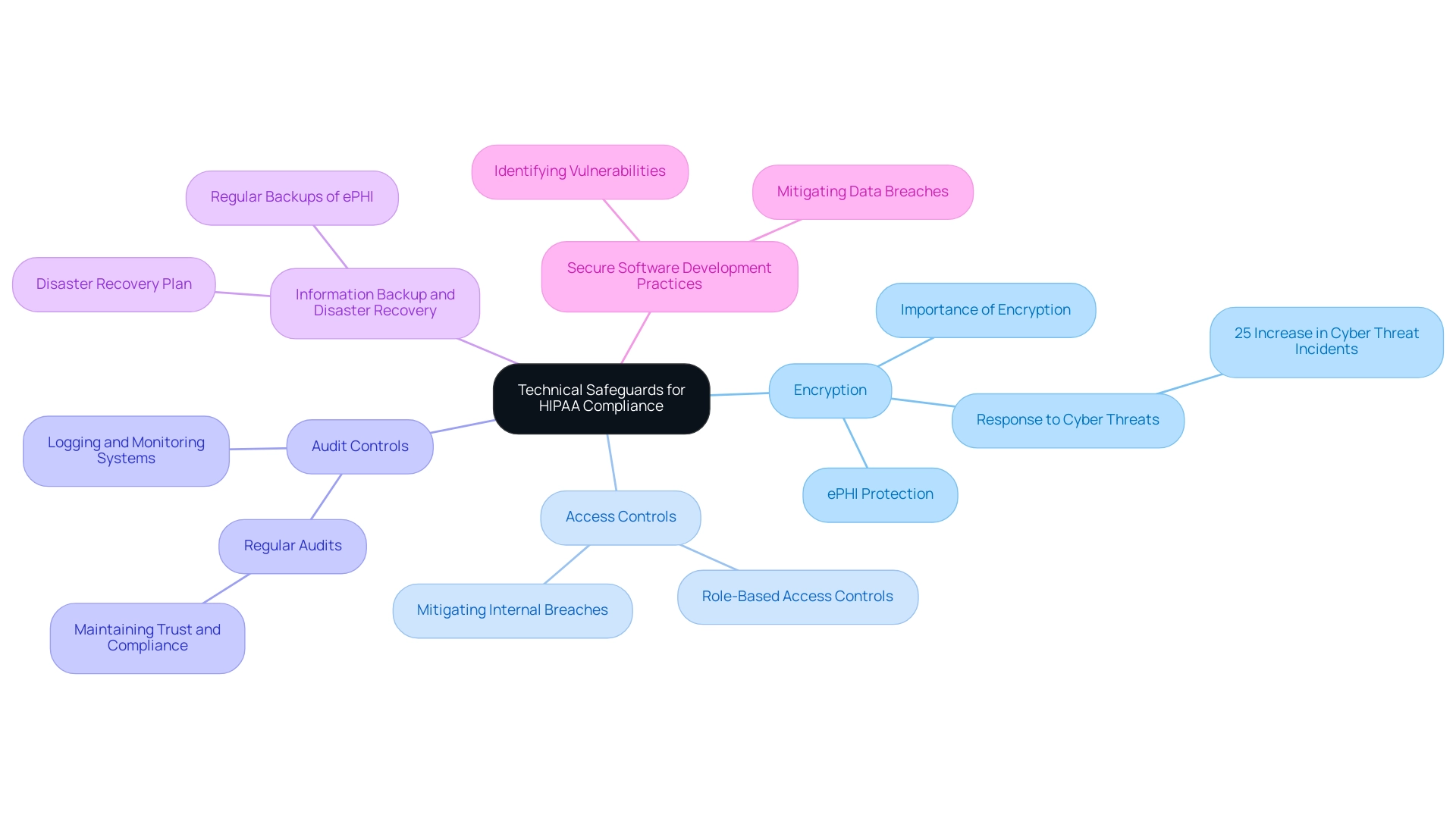
To achieve HIPAA compliance for web applications, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive set of technical safeguards designed to protect electronic Protected Health Data. Key measures include:
- Encryption: It is crucial to encrypt ePHI both in transit and at rest. This practice shields sensitive data from unauthorized access, particularly in light of the 25% increase in reported cyber threat incidents, which has heightened the demand for robust encryption solutions. As Tajammul Pangarkar, CMO at Prudour Pvt Ltd, remarks, "In the ever-changing tech environment, the significance of encryption cannot be exaggerated, particularly for confidential information like electronic protected health information."
- Access Controls: Limiting access to electronic Protected Health Information to authorized personnel is essential. Implementing role-based access controls not only helps in managing who can view or modify sensitive information but also mitigates the risk of internal breaches.
- Audit Controls: Establishing logging and monitoring systems is vital for tracking access and modifications to electronic protected health information. This capability allows organizations to conduct audits and detect potential breaches promptly. Tajammul Pangarkar emphasizes that "regular audits are a cornerstone of maintaining trust and compliance in any tech-driven environment."
- Information Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regular backups of electronic protected health information are essential, along with a well-defined disaster recovery plan to ensure restoration in the event of a loss. Such measures are foundational to maintaining operational integrity during unexpected disruptions.
- Secure Software Development Practices: Following best practices in software development is crucial to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that could expose data to breaches. This proactive approach is imperative for safeguarding ePHI against evolving cyber threats.
The real-world consequences of not applying these safeguards can be observed in the case of Providence Health & Services, which settled for $100,000 in 2008 due to non-compliance with health information regulations. This serves as a stark reminder of the financial and reputational risks associated with inadequate security measures. These technical safeguards not only align with HIPAA compliance for web applications but also strengthen the overall security posture of healthcare applications, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive patient information.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to HIPAA regulations is essential for any organization that handles electronic protected health information (ePHI). The act not only establishes rigorous standards for data protection but also plays a crucial role in fostering trust between healthcare providers and patients. With increasing instances of data breaches and the potential for severe penalties, organizations must prioritize compliance to safeguard sensitive information and mitigate risks.
Key compliance rules highlight the importance of:
- Implementing robust security measures
- Conducting thorough risk assessments
- Establishing clear policies and procedures
By adopting comprehensive technical safeguards such as:
- Encryption
- Access controls
- Regular audits
organizations can effectively protect ePHI while ensuring adherence to HIPAA's stringent requirements. The financial implications of non-compliance serve as a stark reminder of the necessity for ongoing vigilance and proactive measures.
Ultimately, achieving HIPAA compliance is not just about meeting legal obligations; it is about committing to the protection of patient data and the integrity of the healthcare system. As the landscape of healthcare technology continues to evolve, organizations must remain dedicated to continuous improvement in their compliance efforts, fostering a culture of accountability and trust that benefits both providers and patients alike.





