Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) has become a game-changer in various industries, revolutionizing business operations and customer experiences alike. However, deploying AR technology comes with its own set of costs and challenges.
In this article, we will explore the expenses tied to hardware and software needs in AR development, the impact of AR on business operations and cost savings, the role of AR in enhancing customer experience and reducing costs, the cost-benefit analysis of implementing AR in various industries, successful AR implementations and their cost implications, the challenges and limitations of AR adoption and their cost implications, and finally, the future of AR and its potential impact on costs. By delving into these topics, we aim to provide valuable insights into the financial intricacies of leveraging AR technology and its transformative potential.
Hardware and Software Costs in AR Development
Augmented Reality (AR) seamlessly blends digital components with our real-world surroundings, but deploying such an immersive experience doesn't come without its costs. For businesses venturing into AR, it's crucial to factor in the expenses tied to both hardware and software needs.
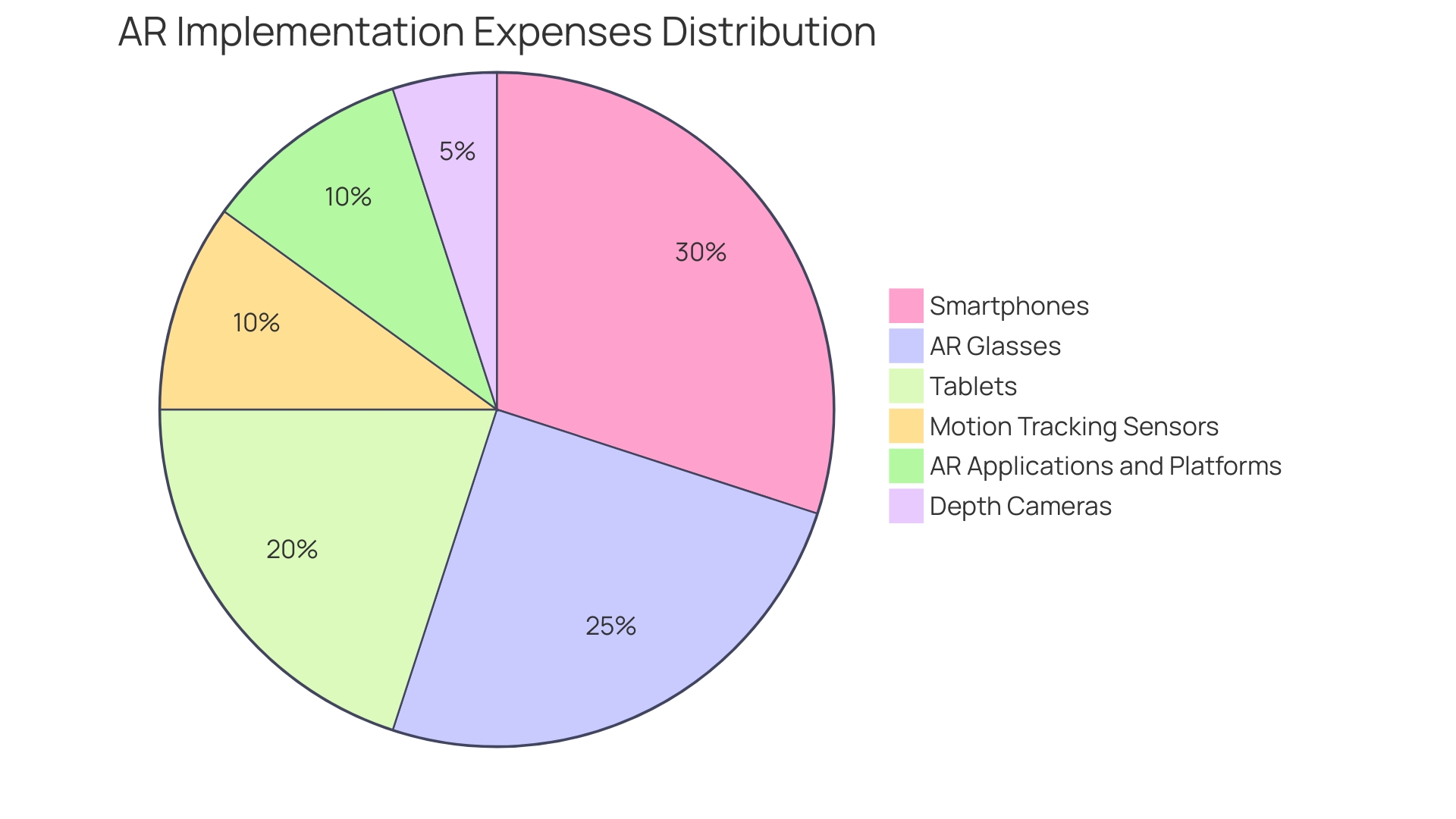
On the hardware front, a range of devices from smartphones and tablets to specialized AR glasses might be necessary. These devices should possess the capability to support AR functionalities.
Moreover, for more intricate AR endeavors, investment in advanced equipment like motion tracking sensors and depth cameras becomes imperative. Switching over to software, there's a spectrum of costs encompassing the creation, development, and licensing of AR applications and platforms. A real-world example worth examining is Meta's production of Quest 3, which highlights that quoted component costs are merely baseline figures and often don't mirror the discounted rates larger corporations may negotiate. This insight underscores the importance of a nuanced budget that accommodates potential cost variations when planning AR implementations.
Impact of AR on Business Operations and Cost Savings
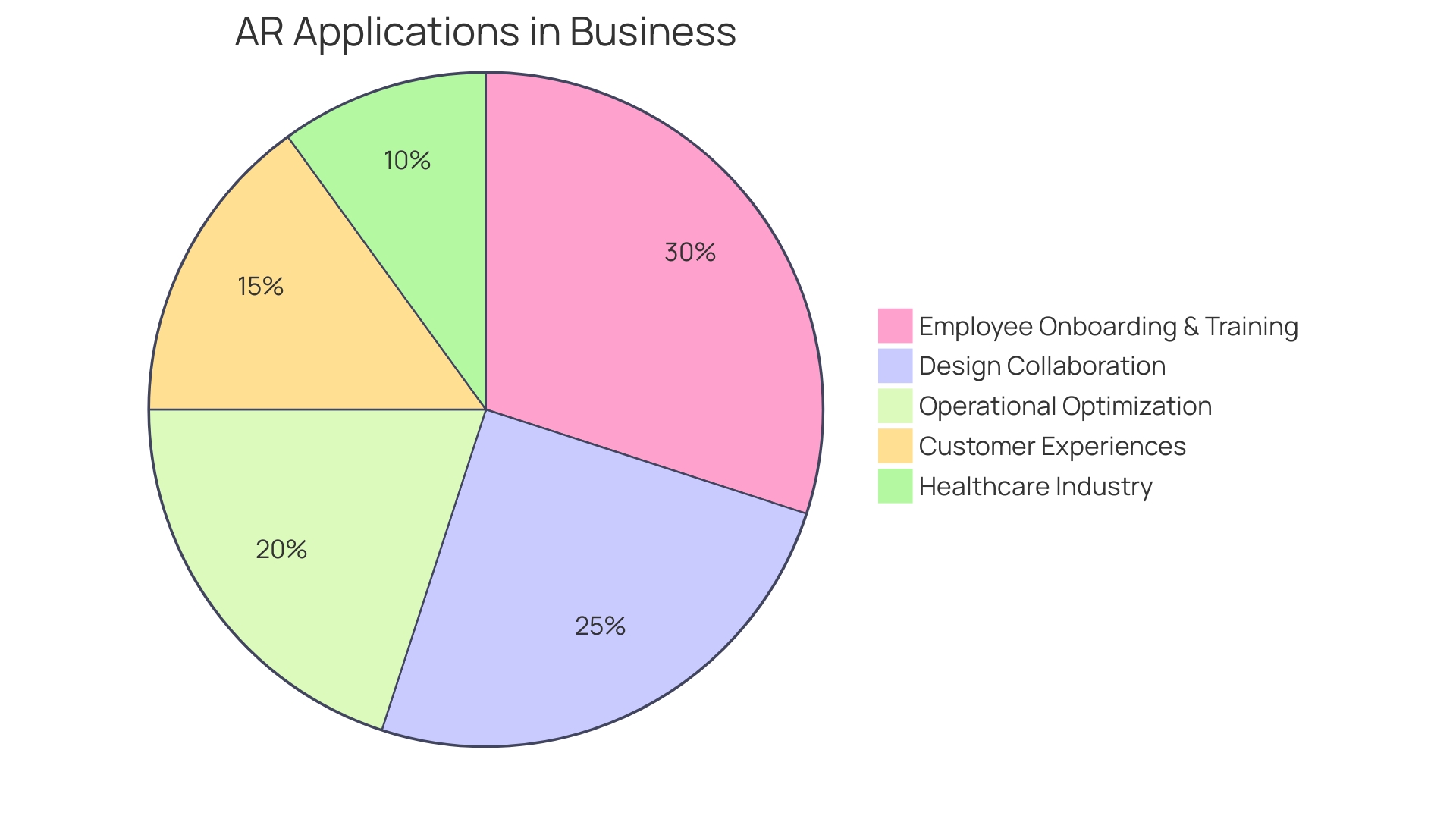
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing the business landscape, offering an interactive experience that elevates the real world with computer-generated enhancements. For instance, industrial automation specialist Tipteh harnessed AR to grant their designers a comprehensive 3D view of machinery during the design process, thereby streamlining collaboration and eliminating misunderstandings. This technological leverage is crucial, especially in an era where the workforce is aging and the loss of critical skills is a significant challenge.
AR facilitates the rapid onboarding and training of new employees, ensuring they are productive without compromising safety or quality, particularly in complex manufacturing and highly regulated industries. The transformative impact of AR is further evidenced by beauty brand Avon, which witnessed a 320 percent surge in conversion rates and a 33 percent increase in average order value after implementing a virtual try-on experience. With AR's ability to enhance training, provide remote assistance, and enrich customer experiences, it's clear that this pillar of Industry 4.0 is not just a futuristic concept but a present-day tool for optimizing operations and achieving cost savings.
The Role of AR in Enhancing Customer Experience and Reducing Costs
Augmented Reality (AR) is rapidly transforming the customer journey, offering a richer, interactive experience that blurs the lines between the digital and physical worlds. Retailers, for instance, are leveraging AR to let customers virtually try on products or envision how furniture might look in their spaces. This not only elevates the shopping experience but also minimizes the likelihood of returns, cutting down on costs.
Beauty brand Avon, for example, witnessed a remarkable 320 percent jump in conversion rates and a 33 percent rise in average order value after incorporating Perfect's AR technology for virtual product try-ons. Furthermore, AR can replace the need for physical samples and printed catalogs with virtual product demonstrations and digital catalogs, leading to significant savings in production and distribution expenses. As the technology becomes more accessible, small businesses are finding AR an invaluable tool to attract and retain customers, creating a new, bold reality that enhances both the assimilation of information and the overall consumer experience.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Implementing AR in Various Industries
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming industries by overlaying digital data onto the physical world, enhancing understanding and productivity. For example, Tipteh, an industrial automation firm, integrated AR to provide their designers with a comprehensive 3D view of machinery during the design process, streamlining collaboration and reducing errors. The adoption of AR in sectors like healthcare is growing, with a significant investment surge from major corporations like Facebook and Samsung.
The benefits of AR are not limited to just one industry; it's an asset across various sectors such as retail, real estate, manufacturing, and entertainment, improving customer engagement and operational efficiency. When evaluating AR implementation, it's essential to weigh the costs against these potential advantages. AR is not just a technological advancement but a strategic tool that, when integrated into business processes, can yield a high return on investment by bridging the gap between digital information and the physical world.
Case Studies: Successful AR Implementations and Their Cost Implications
When delving into the intricate world of augmented reality (AR) and its cost implications, it's instructive to look at Tipteh, an industrial automation specialist. The company, grappling with the complexities of transforming ideas into efficient machines, adopted AR to provide designers with a comprehensive 3D view of their creations.
This allowed for meticulous collaboration, minimized errors, and adhered to ergonomic standards without the burden of extra costs or time-consuming iterations. Similarly, Swisscom's AR campaign targeting the under-40 demographic is a testament to how AR can enhance visibility and brand equity, especially when launching new consumer services.
The adoption of AR is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It requires a thorough initial assessment, ensuring the technology is secure and compliant, as well as checking for pre-existing solutions within the organization.
This echoes the sentiments from the NHS, where technology requests often reveal existing, underutilized resources. Moreover, AR is poised to address critical workforce challenges. As the current workforce ages, the onboarding and training of new employees become paramount, especially in industries with complex manufacturing processes. AR serves as a constant guide, offering real-time instructions and risk assessments, thereby expediting the learning curve while maintaining high standards of safety and product quality. By understanding these diverse applications and the tangible benefits they provide, businesses can better gauge the potential costs and savings associated with AR integration into their operations.
Challenges and Limitations of AR Adoption and Their Cost Implications
Adopting Augmented Reality (AR) technology presents significant opportunities for businesses to enhance their processes and operations. However, this innovation does not come without its challenges.
Technical difficulties, user adoption hurdles, and the necessity for continuous maintenance are just a few of the obstacles that companies may face. These challenges require a strategic allocation of resources to ensure that AR is successfully integrated and utilized.
For instance, Tipteh, an industrial automation specialist, leveraged AR to provide their designers with a comprehensive 3D perspective of machine designs, streamlining the engineering process and reducing costly iterations. As AR becomes a fundamental interface between humans and machines, it's imperative for businesses to invest in training and development to familiarize their workforce with AR technologies.
Furthermore, regular updates and maintenance are crucial to keep up with the evolving AR landscape. The recent growth in the AR market, as evidenced by significant investments from major corporations, underscores the technology's potential across various industries, including healthcare, aerospace, and consumer electronics. With companies like Swisscom utilizing AR to boost brand visibility, it's clear that AR's interactive experience can meet specific business needs in innovative ways. As AR continues to shape Industry 4.0, understanding its potential costs and challenges is essential for businesses aiming to harness its transformative power effectively.
Future of AR and Its Potential Impact on Costs
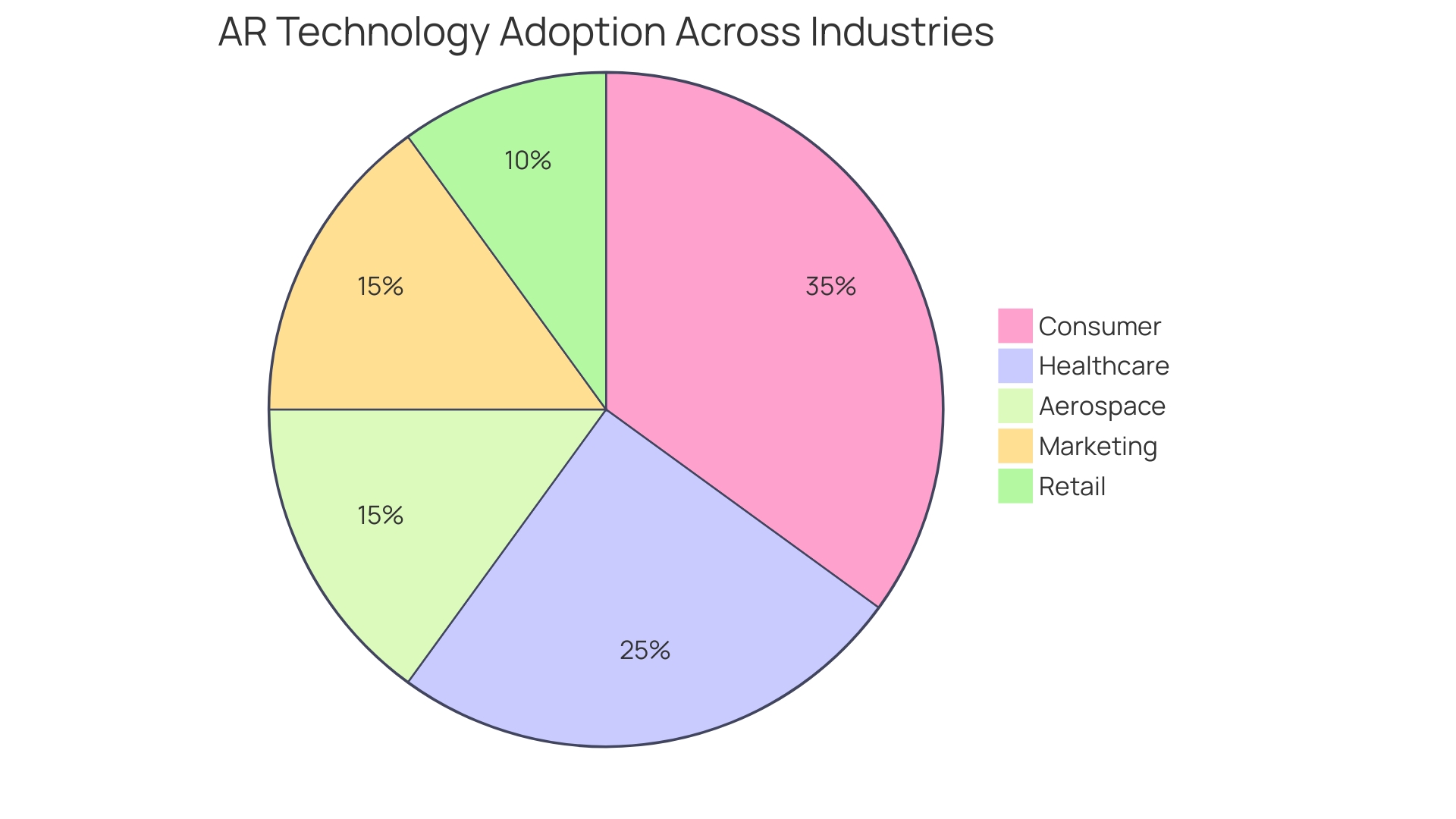
The landscape of Augmented Reality (AR) is rapidly transforming, fueled by substantial investment from tech giants like Facebook Corporation and Intel Corporation, as well as from private firms, venture capitalists, and even government funding. This influx of capital is driving innovation, making the technology more accessible, and, as a result, more cost-effective. Industries ranging from consumer to aerospace, healthcare, retail, and marketing are increasingly integrating AR to enhance operations and customer experiences.
A case in point is Tipteh, an industrial automation specialist, which harnessed AR to provide its engineers with a real-time 3D view of machine designs, thereby saving time and reducing costs. Similarly, Swisscom leveraged AR to boost its brand visibility and connect with a younger demographic. With AR's ability to overlay digital data onto the physical world, it bridges the gap between our three-dimensional reality and the two-dimensional data on our screens.
The recent white paper 'AR as a Booster for Industry 4.0' from HoloLight underscores the transformative impact of AR, highlighting its potential to revolutionize industry processes and improve quality and productivity. As this technology progresses, it promises to unlock new applications and contribute to economies of scale, further decreasing costs and encouraging widespread adoption. For those interested in the financial intricacies of AR, detailed reports offer insights into the costs of components, providing a deeper understanding of the economic factors at play in the production of AR hardware like Meta's Quest 3.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Augmented Reality (AR) technology presents both costs and challenges for businesses. Hardware and software expenses must be considered, along with the need for devices that support AR functionalities and the creation of AR applications. However, the impact of AR on business operations and cost savings is significant.
It streamlines collaboration, enhances productivity, and improves customer experiences. Successful case studies demonstrate how AR can enhance visibility, brand equity, and safety standards. Implementing AR requires a cost-benefit analysis across industries.
It serves as a strategic tool that bridges the gap between digital information and the physical world, offering high returns on investment. Despite challenges like technical difficulties and user adoption hurdles, the future of AR is promising. Substantial investments are driving innovation, making it more accessible and cost-effective.
Industries are integrating AR to optimize operations and enhance customer experiences. Understanding the financial intricacies of leveraging AR technology is crucial for businesses. By carefully assessing costs and potential impacts on operations, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing AR.
In summary, while there are costs involved in deploying AR technology, its transformative potential for businesses is undeniable. By conducting cost-benefit analyses and addressing challenges, companies can harness the power of AR to optimize operations, improve customer experiences, and achieve cost savings. The future of AR looks bright as it continues to evolve and contribute to economies of scale while becoming more affordable.





