Introduction
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing industries across the board, from manufacturing to healthcare, transportation, and beyond. This transformative technology involves the convergence of advanced sensors and devices that capture real-time data and convert it into actionable digital insights.
IIoT applications enable industries to enhance operational efficiency, improve safety protocols, optimize energy consumption, and make data-driven decisions. However, the adoption of IIoT is not without its challenges, including connectivity, data security, and interoperability concerns.
In this article, we will explore the key components of IIoT systems, the applications of IIoT in various industries, the benefits it offers in terms of efficiency, safety, and sustainability, as well as the challenges and limitations of IIoT adoption. We will also delve into the future of IIoT, discussing emerging trends and predictions that are shaping the manufacturing and production landscape. Join us on this journey to understand how IIoT is transforming industries and paving the way for a more connected and intelligent future.
What is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
At the heart of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the convergence of advanced sensors and devices that capture critical data from the physical world, transforming it into actionable digital insights. This technology is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0—a revolutionary wave of automation that integrates digital systems with physical operations across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture.
IIoT applications are instrumental in real-time monitoring and control, enhancing the agility and efficiency of industries. They enable detailed oversight of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and motion, facilitating preemptive maintenance in manufacturing plants or optimizing energy consumption in the utility sector.
Moreover, IIoT's reach extends well beyond traditional industries. In healthcare, it enhances patient care through advanced monitoring systems, while in transportation, it improves safety and efficiency through data-driven decision-making.
Nonetheless, the journey to full IIoT adoption is not devoid of challenges, with concerns around connectivity, data security, and interoperability at the forefront. Despite these hurdles, the overall impact of IIoT is transformative, fostering more connected and responsive industrial environments. Recent news underscores the transformative potential of IIoT, with initiatives like the UK government's investment in multi-purpose street columns that facilitate the expansion of wireless networks and offer public WiFi. These smart infrastructures, capable of charging electric vehicles and boosting connectivity, exemplify the innovative applications of IIoT in urban settings. Such advancements signal a future where IIoT's role in enhancing operational efficiency and service delivery is both pivotal and ubiquitous.
Key Components of IIoT Systems
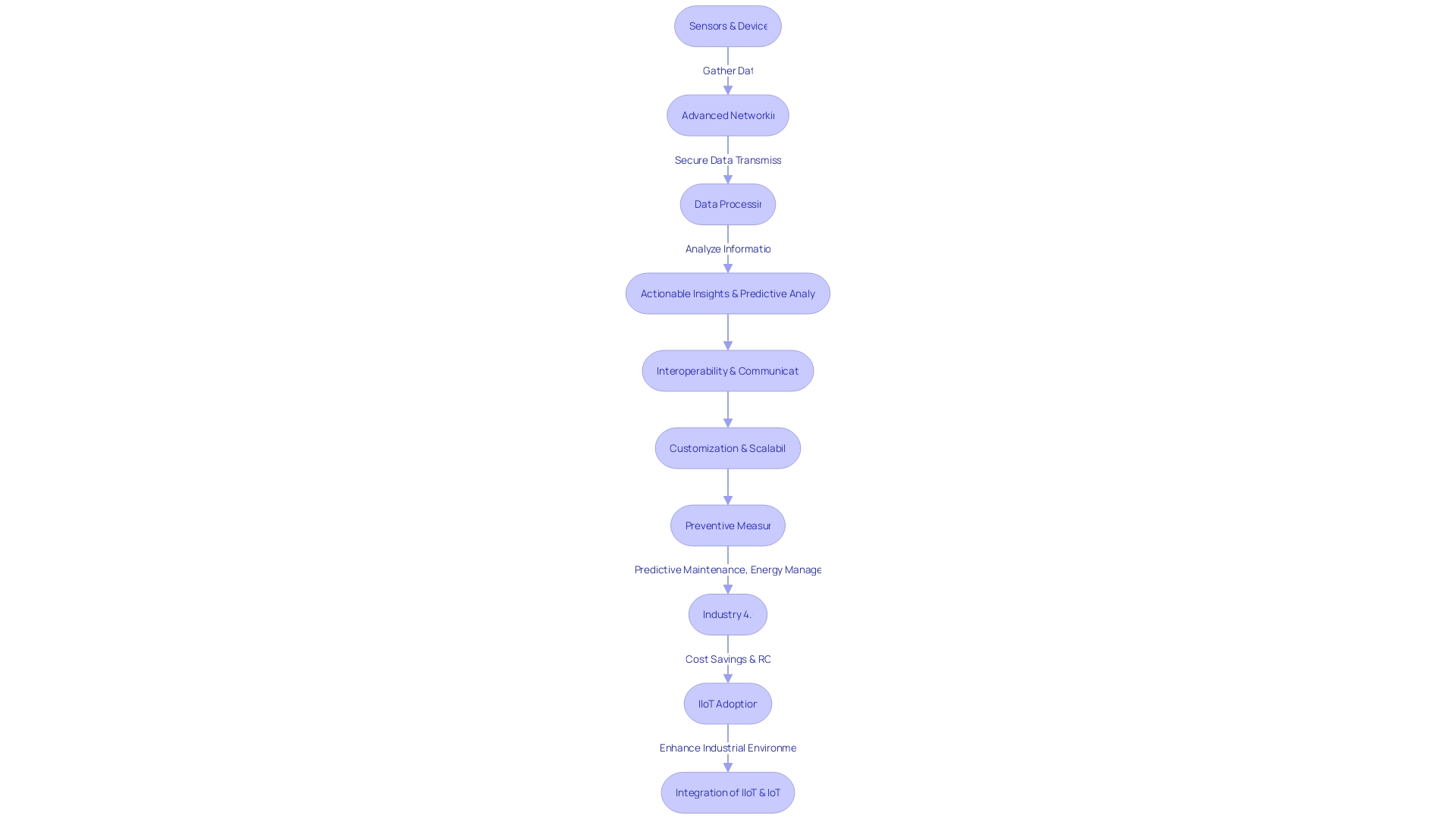
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems are transformative, enabling industries to become more connected, efficient, and agile. At the heart of these systems are sensors and devices that gather data on parameters like temperature, pressure, and motion.
This data is then transmitted through advanced networking technologies, ensuring secure data flow. Sophisticated data processing capabilities are essential to organize and analyze this information, allowing for actionable insights and predictive analytics that forecast future trends and anomalies.
Interoperability is crucial in IIoT, as platforms must communicate with a diverse array of devices. This flexibility allows businesses to customize their IIoT solutions to their specific needs, fostering scalability.
The connected nature of these systems empowers industries to implement preventive measures, improving safety and efficiency. For example, predictive maintenance can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, while energy management systems optimize usage to cut utility bills. Despite challenges surrounding connectivity and data security, the adoption of IIoT is driving the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0. With the potential for significant cost savings and ROI, industries are leveraging IIoT to revolutionize their operations. As noted by industry leaders, the integration of IIoT into business models is not an either/or decision but a strategic move that combines the strengths of both IIoT and traditional IoT applications to enhance industrial environments.
Applications of IIoT in Various Industries
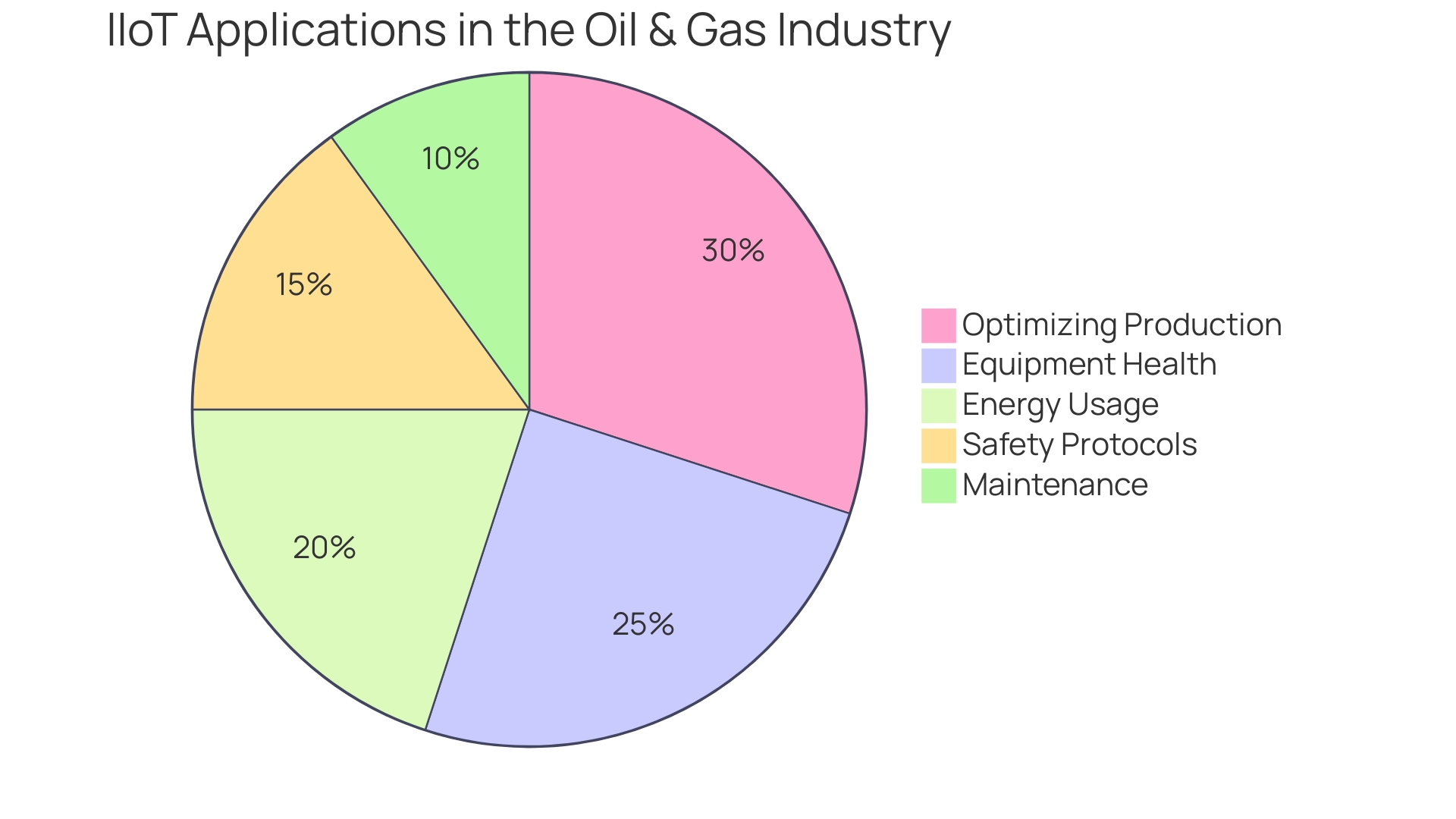
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing sectors far beyond its roots in manufacturing. It's a pivotal element in the oil and gas industry, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
By leveraging IIoT, companies can optimize production and proactively maintain equipment health, thus preventing costly downtimes and hazardous incidents. Through real-world case studies, industry professionals have witnessed the transformative power of IIoT in optimizing energy usage and maintenance, as well as improving safety protocols.
With a focus on scalability, IIoT solutions are designed to grow with the business, ensuring that investments made today will continue to yield benefits as technology progresses. As industries recognize the need for interconnected, efficient operations, the adoption of IIoT is accelerating, despite challenges such as data security and interoperability. The key to successful IIoT deployment lies in starting with a manageable pilot project to demonstrate value before expanding the technology's reach across the organization. This strategic approach allows for a tailored application of IIoT that aligns with specific operational goals and KPIs, such as increased Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) or reduced quality defects.
Benefits of IIoT: Efficiency, Safety, and Sustainability
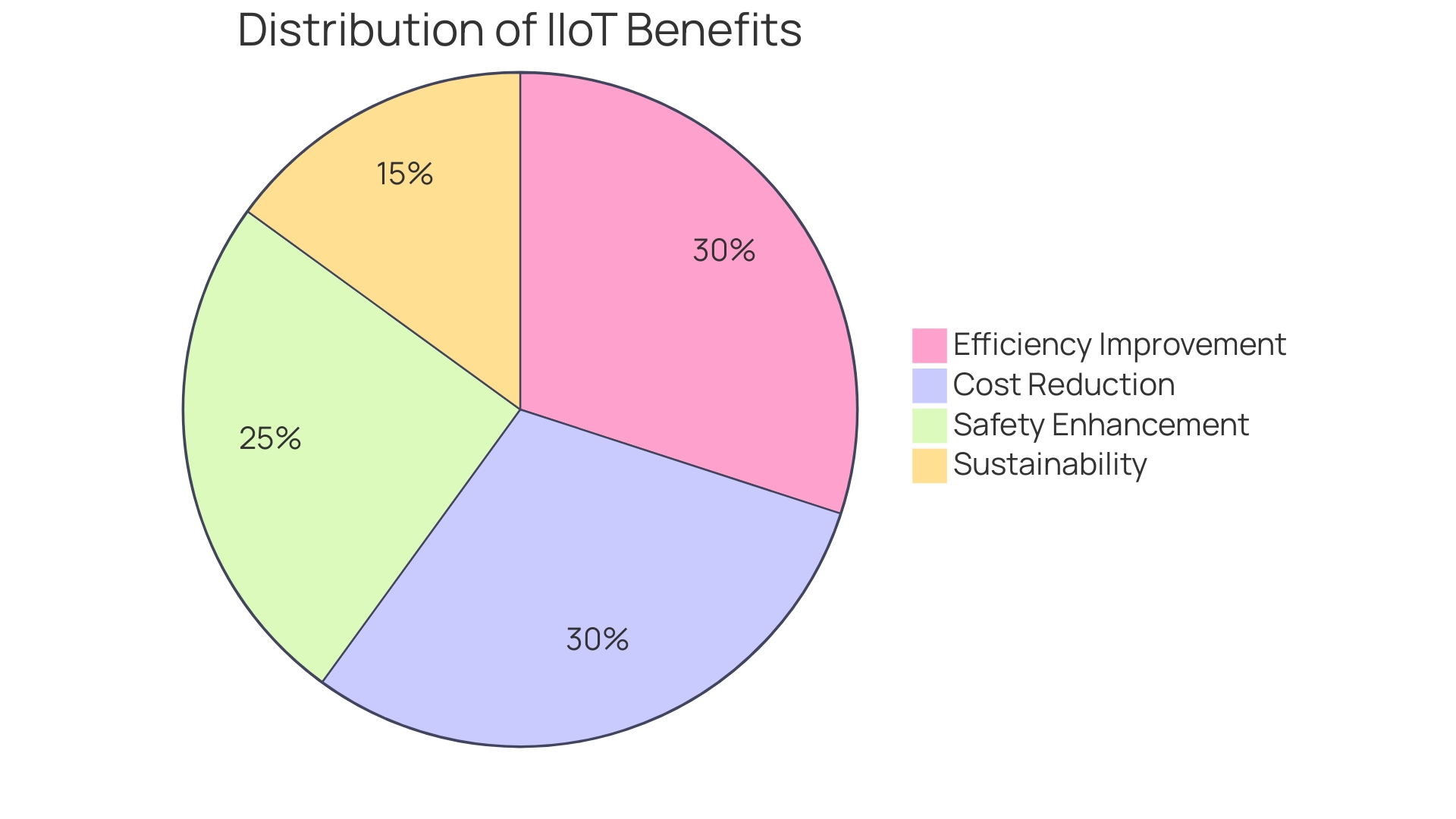
Harnessing the power of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) transcends traditional operational methods, providing a pathway to remarkable improvements in efficiency, safety, and sustainability, while enabling data-driven decisions that are critical in today's fast-paced industrial environment. Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance facilitated by IIoT technologies are not just theoretical constructs but have been practically applied in Schneider Electric's smart factories.
The deployment of EcoStruxure Plant Lean Management has demonstrated operational efficiency improvements up to 5%, a 33% reduction in shift handover activities, and three times faster issue resolution. These advancements are built on an open, scalable, and cyber-secure IIoT platform, illustrating the tangible benefits of digital transformation.
The integration of LoRaWAN technology exemplifies how low-cost, easily deployable networks can revolutionize industrial operations. By supporting a wide array of use cases, from resource management to safety enhancement, this technology ensures privacy and coverage even in the most remote areas.
The move towards digitization is further underscored by the need for solutions that convert the mere 5% of plant data currently used into actionable insights, as revealed by a study from AWS and Frost & Sullivan. EcoStruxure Plant Lean Management represents a significant step in this direction, providing accessible real-time data to facilitate quick and efficient problem-solving.
Furthermore, the predictive maintenance market, which has reached $5.5 billion, is driven by the need to reduce operational costs and the desire for solutions that offer a positive return on investment. The importance of IIoT in achieving these financial goals cannot be overstated, as it empowers companies to avoid costly equipment failures and unnecessary maintenance interventions. This proactive approach is essential for industries that are increasingly reliant on complex equipment, such as offshore wind turbines, where the design and operation challenges are amplified by the need for higher capacity and efficiency. In the broader context of sustainability, IIoT plays a pivotal role in advancing the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in the transition towards renewable energy. IoT-enabled devices offer real-time insights into energy consumption and production efficiency, enabling businesses to optimize energy generation and integrate renewable sources effectively. By embracing IoT technologies, industries not only progress towards a clean energy future but also contribute to the global effort to mitigate climate change and promote environmental stewardship.
Challenges and Limitations of IIoT Adoption
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) offers transformative potential for e-commerce, yet it comes with its own set of challenges. Interoperability is a critical factor, as it ensures that various systems and devices can seamlessly communicate and work together.
Without it, companies face the risk of siloed data, losing valuable insights and optimization opportunities. Cybersecurity is another significant concern; with IIoT, safeguarding data against unauthorized access is paramount.
This includes utilizing end-to-end encryption and conducting regular software updates and staff training on data security. Scalability and cost are further considerations.
Cloud computing can address scalability, allowing for efficient data and device management, while also potentially reducing costs associated with data storage and management. However, the initial investment can be substantial.
As reported by a strategy director from a Spanish electronics company, gathering the necessary funds for an IIoT initiative can be a lengthy and challenging process, with 20% of organizations citing budget constraints as a major hurdle. This is reflected in the longer timelines associated with IIoT projects, where even developing a business case can take up to 9 months, as compared to 6 months for more straightforward approaches. The approach to IIoT implementation is also evolving. Recent trends indicate a shift towards purchasing complete, standardized IIoT solutions, with 30% of projects initiated in 2021 or 2022 favoring this 'buy' approach, up from 9% in previous years. This shift suggests that companies are increasingly seeking plug-and-play solutions that minimize the need for extensive IT involvement and can deliver business outcomes more rapidly. In conclusion, while the benefits of IIoT for e-commerce are clear, successful adoption requires careful consideration of interoperability, data security, scalability, and cost, as well as a strategic approach to implementation that aligns with the organization's capabilities and resources.
Future of IIoT: Trends and Predictions
As the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) continues to evolve, we are witnessing a convergence of cutting-edge technologies that are shaping the future of manufacturing and production. Edge computing is revolutionizing how data is processed, allowing for real-time analytics and decision-making at the site of data collection.
This mitigates latency issues that can hinder critical operations, particularly in sectors where immediate response is essential, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation systems. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are also playing pivotal roles.
By analyzing the vast datasets generated by IIoT, these technologies enable predictive maintenance and resource optimization, leading to smarter, more efficient operations. However, with this surge in connectivity, there is a marked increase in cyber threats, including ransomware.
It's imperative that IT, OT, and security teams collaborate to fortify cybersecurity measures and protect not only the data but also the well-being of employees. The emergence of 5G connectivity is set to further accelerate IIoT capabilities with its high-speed and reliable communication, while blockchain technology promises enhanced security and traceability across the supply chain.
These advancements come amidst a backdrop of growing industry collaboration, as evidenced by the success stories and best practices shared in our comprehensive case studies. Moreover, the semiconductor industry's shift towards AI chipsets and IoT connectivity, despite the challenges of chip shortages, underscores the vital role of these components in the IIoT ecosystem. The takeaway for companies, even those not yet ready to fully embrace these technologies, is the importance of data collection. With the adage 'Data is the new oil,' businesses are advised to amass operational data now to refine AI models later for precise, use-case specific applications, thereby avoiding the cost of missed opportunities. In summary, the integration of these technologies not only promises a more interconnected and intelligent industrial environment but also necessitates a proactive approach to data management and cybersecurity to harness the full potential of IIoT.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing industries by capturing real-time data and converting it into actionable insights. It enhances operational efficiency, improves safety protocols, optimizes energy consumption, and enables data-driven decision-making. Despite challenges like connectivity, data security, and interoperability concerns, IIoT is transforming industries and fostering more connected and responsive environments.
The key components of IIoT systems include sensors and devices for data capture, advanced networking technologies for secure data flow, sophisticated data processing capabilities for actionable insights, and interoperability for customization and scalability. IIoT has applications beyond traditional industries. It enhances patient care in healthcare and improves safety and efficiency in transportation through data-driven decision-making.
The benefits of IIoT are remarkable improvements in efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Challenges of IIoT adoption include interoperability issues, cybersecurity concerns, scalability considerations, cost constraints, longer timelines associated with projects. The future of IIoT is shaped by cutting-edge technologies such as edge computing for real-time analytics at the site of data collection.
AI and ML enable predictive maintenance and resource optimization. 5G connectivity accelerates IIoT capabilities while blockchain technology enhances security and traceability across the supply chain. In summary, by addressing challenges while embracing opportunities brought by IIoT adoption, industries can pave the way for a more connected future.
The integration of these technologies promises a more interconnected and intelligent industrial environment. A proactive approach to data management and cybersecurity is necessary to harness the full potential of IIoT. With its transformative impact on industries across sectors, IIoT is shaping a more efficient, safe, sustainable future.





