Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of mobile app development, choosing the right tools can be the defining factor between success and stagnation. With the market projected to reach an astounding $8.1 trillion by 2026, developers must navigate a complex landscape that includes:
- Native tools
- Cross-platform solutions
- The burgeoning realm of no-code and low-code platforms
Each category offers distinct advantages tailored to various project needs, from optimizing user experience to expediting development timelines. As organizations increasingly embrace these technologies, understanding their unique features and implications becomes essential for harnessing innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
This article delves into the diverse array of mobile app development tools available today, providing insights into their capabilities and guiding developers in making informed choices that align with their strategic goals.
Overview of Mobile App Development Tools
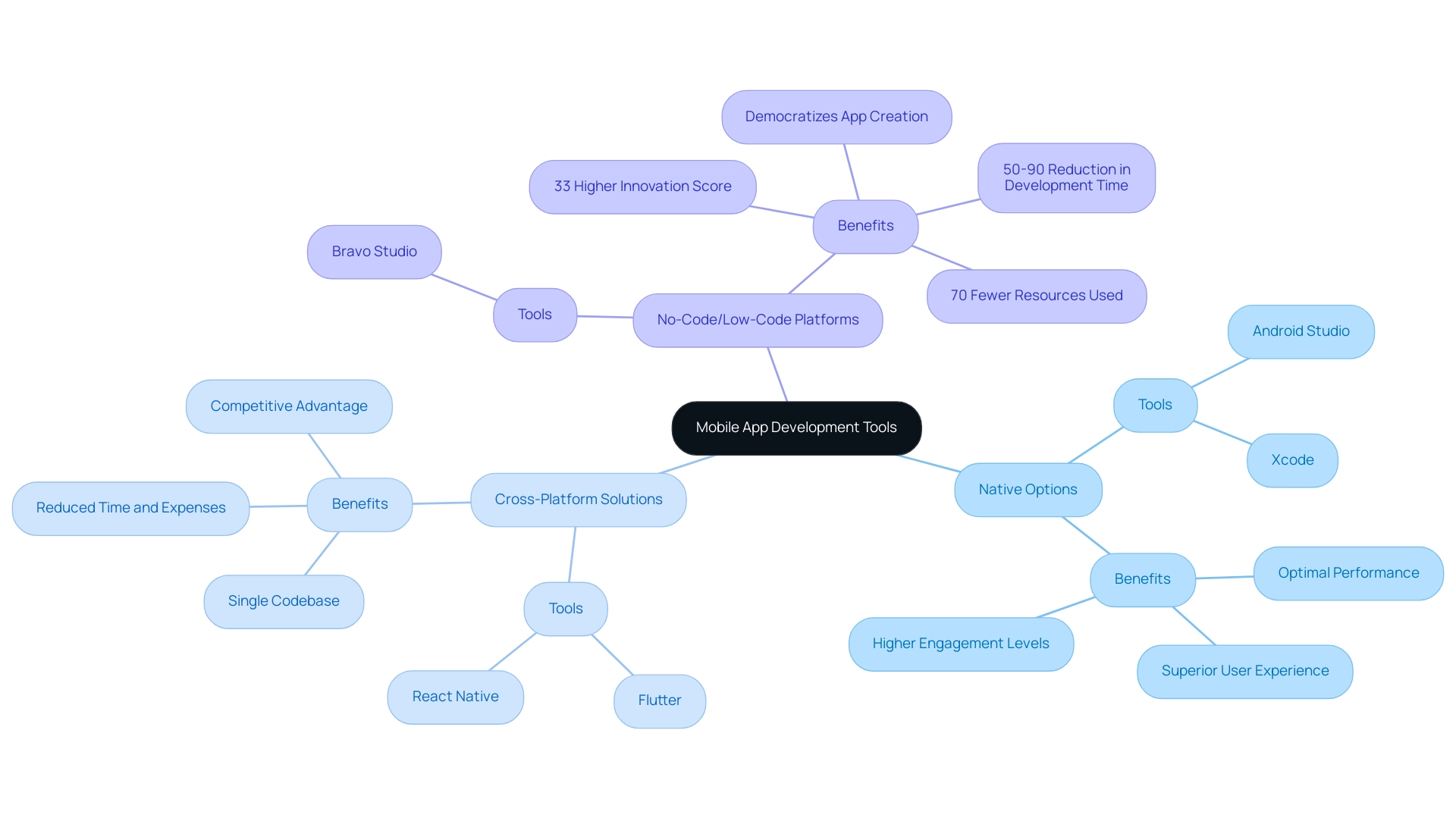
The resources for mobile application creation can be categorized into three main groups, which include tools to develop mobile apps: native options, cross-platform solutions, and no-code/low-code platforms.
-
Native software, such as Android Studio and Xcode, are designed for specific operating systems, delivering optimal performance and a superior user experience. This specialization often results in higher engagement levels among users, which is critical as the e-commerce market is projected to reach an impressive $8.1 trillion by 2026.
-
Cross-platform solutions, such as Flutter and React Native, enable developers to create applications for multiple platforms from a single codebase, significantly reducing both time and expenses. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in a fast-paced market where speed to market can determine competitive advantage.
-
No-code and low-code platforms, like Bravo Studio, serve as tools to develop mobile apps for individuals with limited coding abilities, thereby democratizing the app creation process.
This shift not only expands the talent pool for app creation but also caters to a broader audience of entrepreneurs and enterprises, enhancing innovation across sectors. As organizations progressively embrace low-code solutions, they report an impressive 33% higher innovation score compared to conventional methods, with creation times cut by 50-90% and resource use reduced by up to 70%. A specific case study highlights that organizations leveraging low-code solutions can build cloud-native apps up to 10 times faster while using 70% fewer resources, which profoundly impacts productivity and job satisfaction.
Additionally, according to Statista, gaming apps account for 28% of the apps available in China, illustrating the competitive landscape of the app market. The recent increase in Google Play Store downloads by 31%, in contrast to only 2.5% for the Apple App Store from 2019 to 2020, further highlights the current trends in app usage, making these resources vital for contemporary app creation.
Top Cross-Platform Development Tools
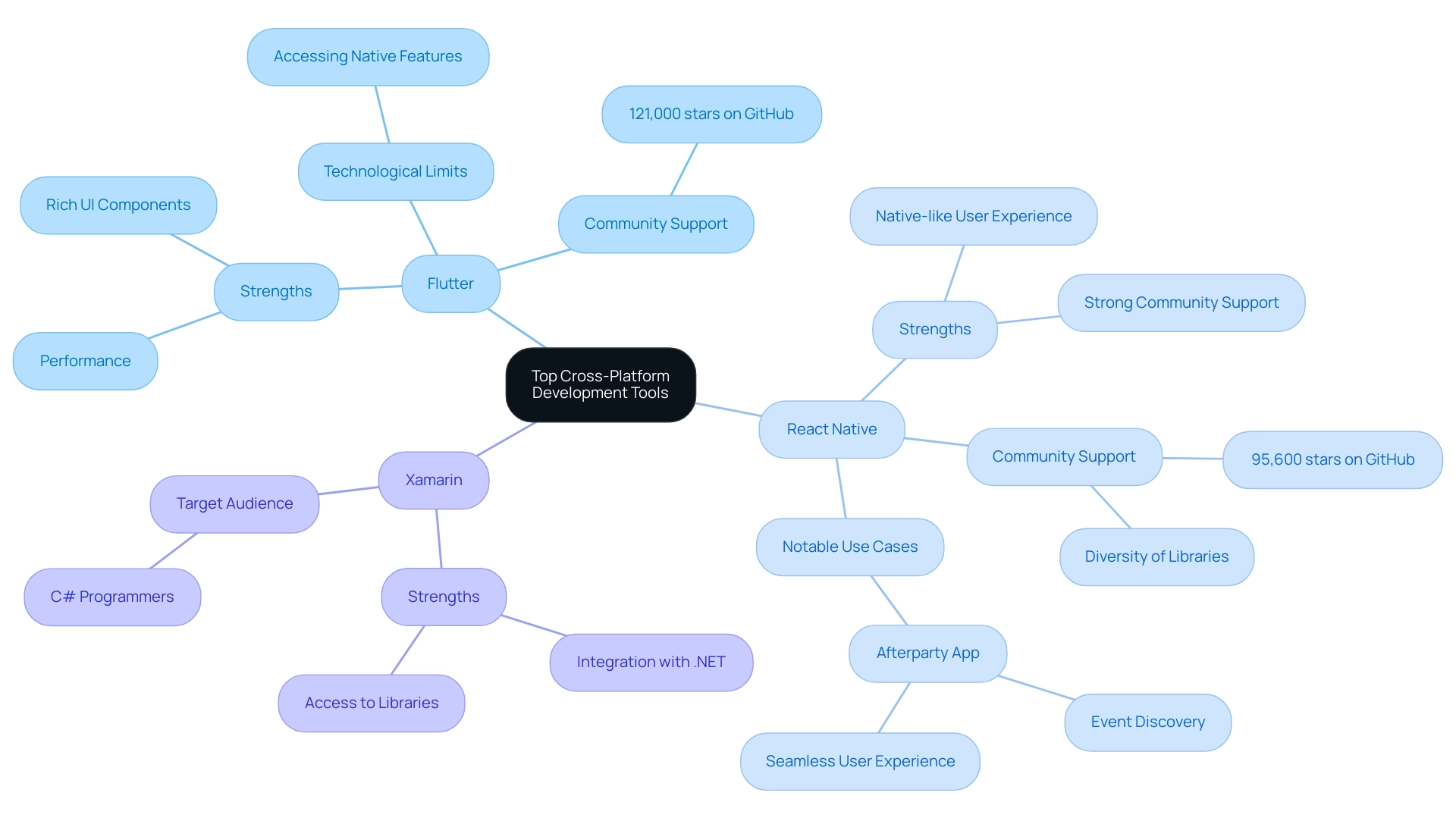
In the competitive landscape of cross-platform development tools, Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin each provide unique strengths tailored to different project requirements and programmer proficiencies. Flutter, developed by Google, is famous for its remarkable performance and rich UI components, allowing creators to design highly customizable applications that stand out in functionality and aesthetics. However, it may face certain technological limits, particularly when it comes to accessing native device features, which can impact its usability for complex applications.
As of May 2022, Flutter has garnered significant community support, boasting 121,000 stars on GitHub, surpassing React Native's 95,600 stars, indicating its growing popularity among programmers.
React Native, backed by Facebook, is celebrated for delivering a native-like user experience, making it a preferred choice for many mobile application creators. Its strong community offers abundant resources and support, which is essential for individuals navigating challenges during app development. However, the diversity of libraries available in React Native can lead to variations in quality and support, which programmers should consider.
A notable example of React Native in action is the Afterparty app, a social networking platform that facilitates event discovery. Leveraging React Native, Afterparty offers users a seamless and intuitive experience for exploring local events, showcasing the framework's capability in real-world applications.
Xamarin, a product of Microsoft, integrates deeply with the .NET framework, making it an appealing option for programmers already versed in C#. This integration offers access to a plethora of libraries and resources, boosting productivity and simplifying the creation process.
As developers consider their choices, particularly those in the e-commerce field, comprehending the unique benefits and drawbacks of each resource is crucial for selecting the appropriate tools to develop mobile apps for their projects.
The Rise of No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
The surge in popularity of no-code and low-code platforms highlights a pivotal moment in the tools to develop mobile apps landscape. These innovative tools to develop mobile apps empower individuals with minimal coding knowledge to create fully functional applications. Platforms like Bravo Studio and Adalo allow users to visually create apps, dramatically shortening timelines and costs.
This capability is especially advantageous for startups and small enterprises, which frequently encounter resource limitations in forming a complete project team. As these platforms continue to evolve, they are not only streamlining the creation process but also offering tools to develop mobile apps, allowing a broader range of individuals to transform their ideas into reality. In 2024, the no-code and low-code market is anticipated to expand considerably, indicating a tectonic shift in how businesses approach application creation.
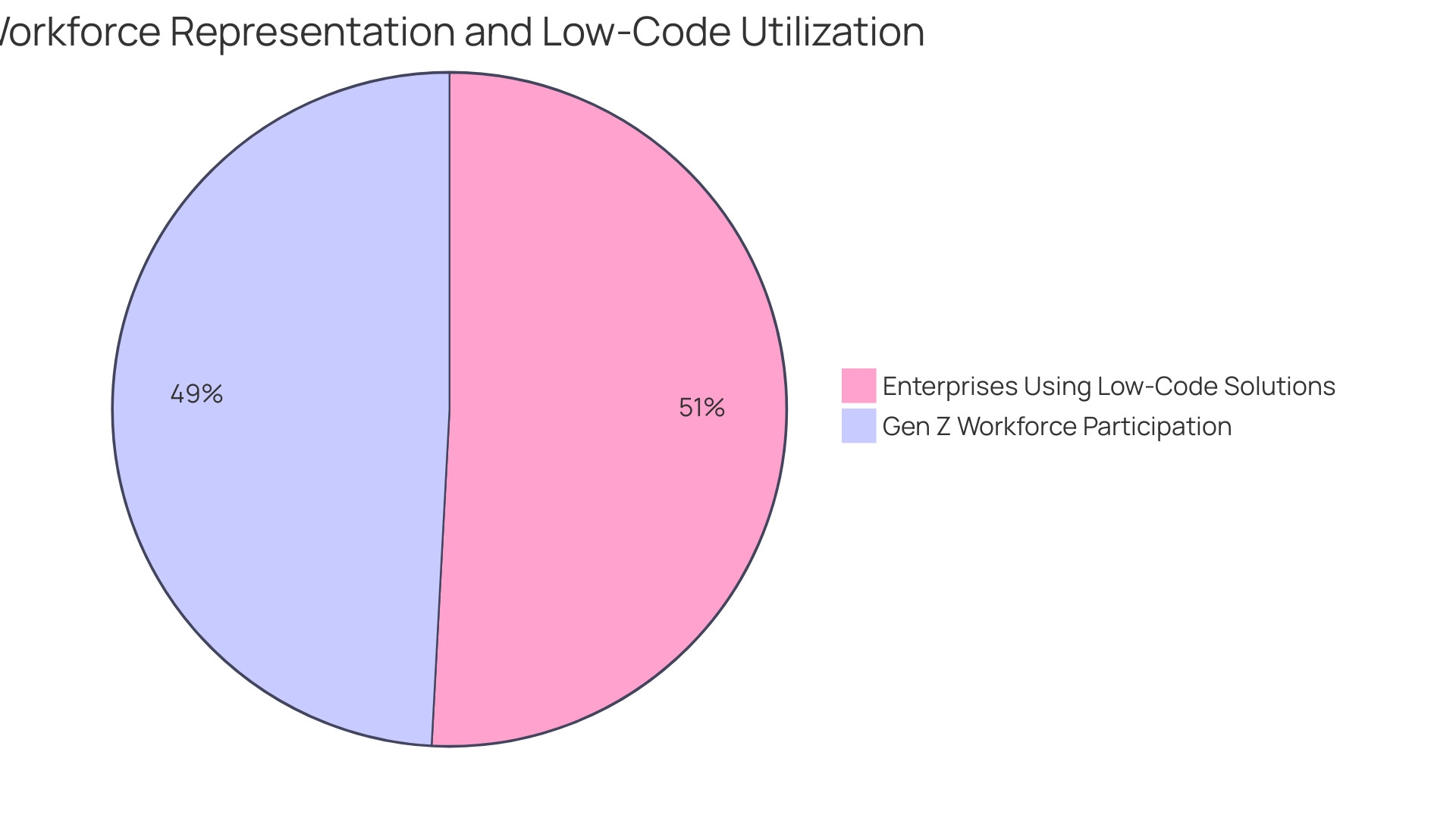
This trend is further supported by the projected growth of the global low-code development market by 23 percent in 2021, underscoring the significance of this movement. Additionally, the increasing participation of Gen Z, who made up 11.6% of the workforce in 2020, is expected to drive innovation within this space. However, challenges such as legacy systems and fears surrounding new technology persist, with only 12% of enterprises managing their business processes using low-code solutions after acquiring them, according to Gartner.
Acknowledging these challenges is essential for modern businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and foster collaboration among domain experts, business users, and developers.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Mobile App Project
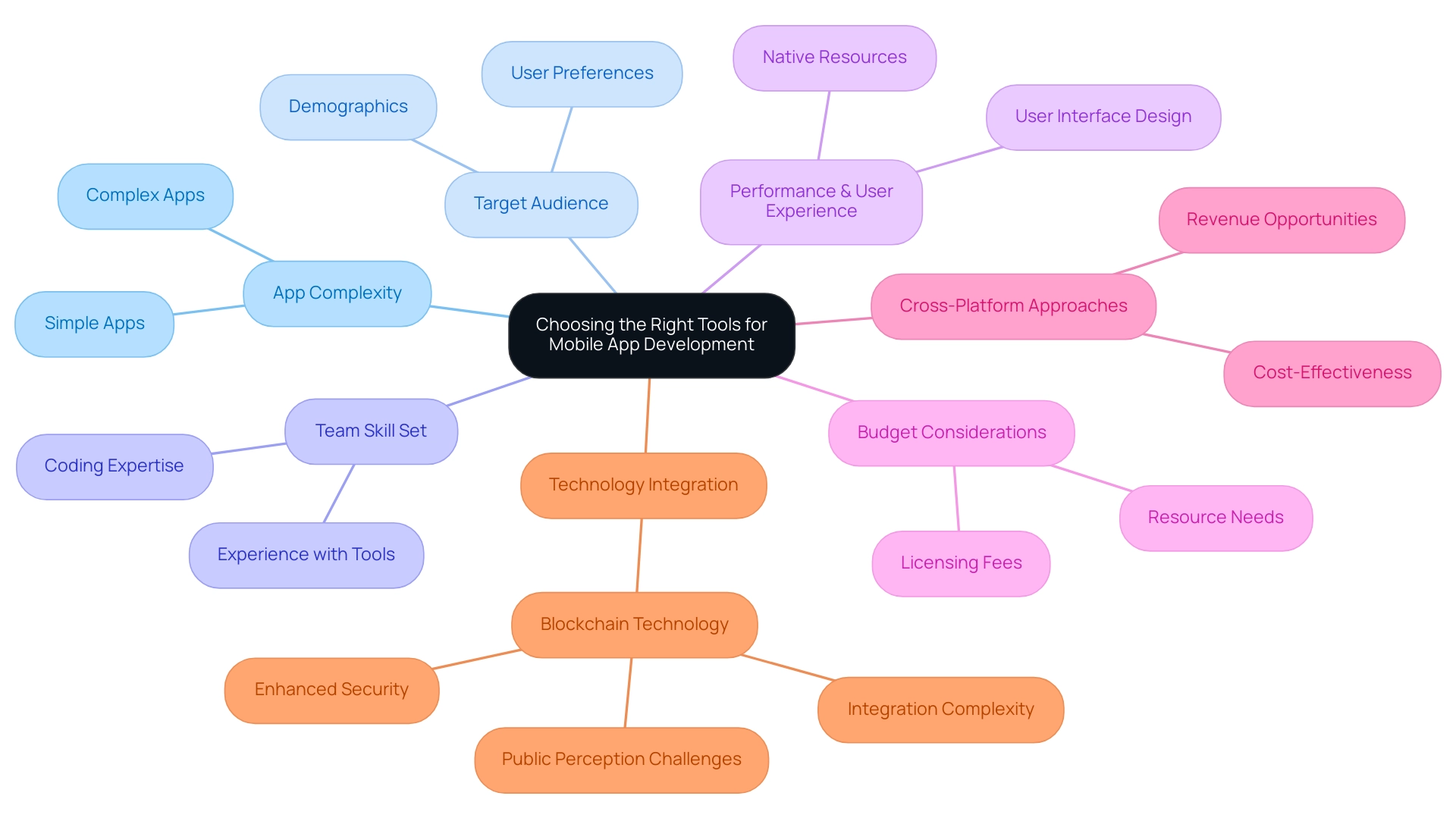
Choosing the appropriate tools to develop mobile apps requires a nuanced comprehension of various key elements, including the app's complexity, the target audience, and the team's skill set. For projects prioritizing rapid progress without extensive coding expertise, using tools to develop mobile apps like no-code or low-code platforms presents an effective solution, allowing for swift iteration and deployment. Conversely, when performance and user experience are crucial, investing in native resources becomes vital, guaranteeing that the final product upholds high standards.
Additionally, budgetary considerations are paramount; many tools entail licensing fees or necessitate supplementary resources that can impact overall project costs. Notably, cross-platform or hybrid approaches can provide cost-effectiveness and revenue opportunities across multiple platforms, making it a compelling choice for budget-conscious projects. As Sarah Johnson, a visionary at FitTech Innovations, aptly noted,
This strategic decision will drive growth and improve our high-quality products and services.
Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology in mobile app development illustrates the potential for enhanced security and transparency in transactions, while also highlighting challenges such as integration complexity and public perception. Ultimately, the alignment of the tools to develop mobile apps with the overarching project objectives is crucial for achieving successful outcomes, paving the way for enhanced efficiency and user satisfaction. Additionally, considering that Berkshire Hathaway’s Class A shares (BRK.A) crossed the $695K mark on August 28, 2024, it underscores the importance of strategic investment in technology to drive growth in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of mobile app development, the selection of appropriate tools is critical to navigating the complexities of the market. With options ranging from native tools that ensure optimal performance to cross-platform solutions that enhance efficiency, developers must weigh the unique advantages each category offers. The rise of no-code and low-code platforms has further transformed the landscape, democratizing app creation and enabling individuals with minimal coding experience to bring their ideas to life. This shift is not just a trend; it represents a fundamental change in how applications are developed, fostering innovation and expanding the talent pool.
As the market for mobile applications continues to grow exponentially, understanding the nuances of each development tool becomes paramount. The choice between native, cross-platform, or no-code solutions should align with the project's specific needs, including complexity, budget, and target audience. By making informed decisions, developers can not only enhance user experience but also drive efficiency and productivity within their teams.
In summary, the future of mobile app development hinges on the strategic selection of tools that resonate with organizational goals and market demands. Embracing the right technology will empower developers to create innovative solutions that stand out in a competitive landscape. As the industry evolves, staying abreast of these developments will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving sustained success in the app economy.





