Introduction
In an age where cyber threats loom larger than ever, the importance of penetration testing cannot be overstated. As organizations grapple with an increasing number of sophisticated attacks, understanding the nuances of ethical hacking has become a critical component of robust cybersecurity strategies.
This article delves into the definition and significance of penetration testing, explores various tools available for effective assessments, and outlines best practices that empower businesses to fortify their defenses. By shedding light on the evolving landscape of vulnerabilities and the tools designed to combat them, this comprehensive guide equips organizations with the knowledge necessary to safeguard sensitive data and maintain trust in an increasingly perilous digital environment.
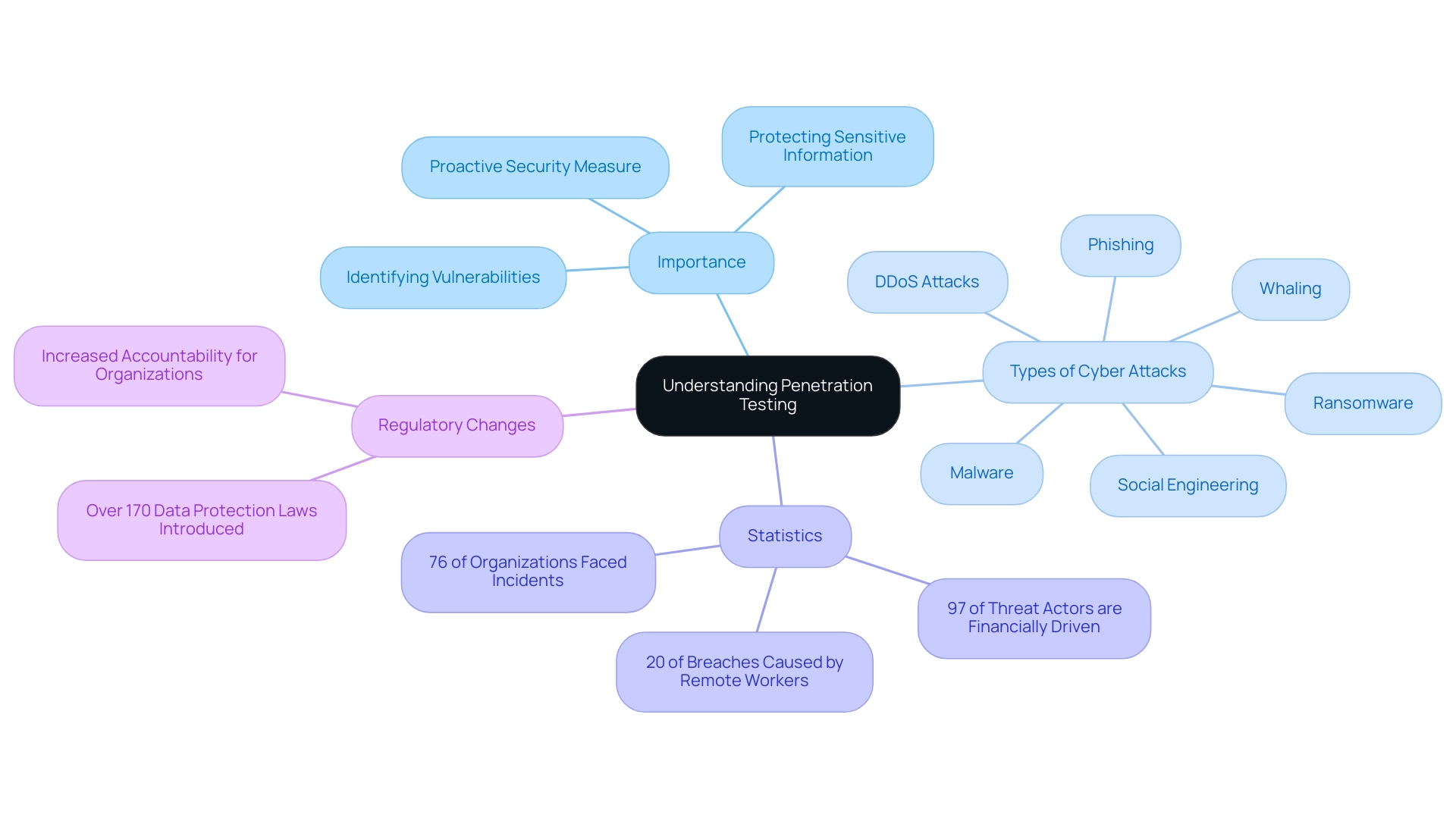
Understanding Penetration Testing: Definition and Importance
Penetration testing, often referred to as ethical hacking, is a crucial practice that involves using tools for penetration testing of web applications to simulate cyber-attacks and identify weaknesses that could be exploited by cybercriminals. This proactive approach is vital for organizations in 2024, particularly as a recent study indicates that 76% of organizations encountered a cybersecurity incident stemming from unaddressed vulnerabilities. The rising frequency of cyber attacks, including:
- phishing
- whaling
- malware
- social engineering
- ransomware
- DDoS attacks
underscores the necessity of this practice.
Moreover, with 97% of threat actors being financially driven, as highlighted in a 2023 data breach investigation report by Verizon, organizations must prioritize security testing to protect sensitive customer information and maintain their reputations in an increasingly hostile digital environment. In response to the growing number of data breaches, over 170 data protection laws were introduced in 2023 and 2024, reflecting a shift towards more stringent data protection measures and increased accountability for organizations. By regularly using tools for penetration testing of web applications, businesses can conduct penetration tests that provide valuable insights into their protective stance, enabling them to rectify weaknesses before they are exploited.
Exploring Different Types of Penetration Testing Tools
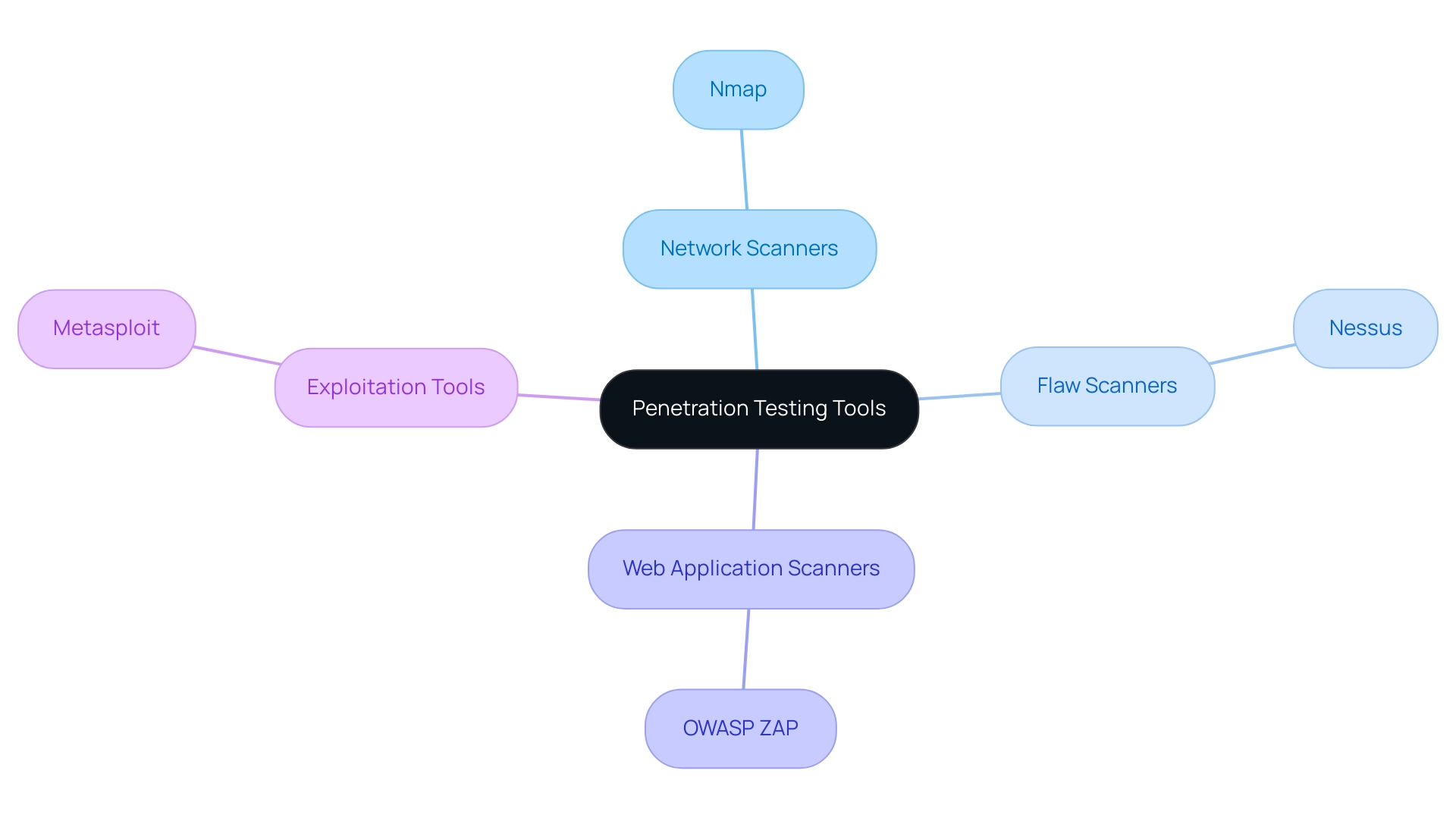
The essential tools for penetration testing of web applications are crucial for identifying weaknesses in both web and mobile applications, and they can be classified into four primary categories:
- Network scanners
- Flaw scanners
- Web application scanners
- Exploitation tools
Network scanners, like Nmap, play a crucial role in identifying active devices and open ports within a network, allowing teams to comprehend their attack surface. Assessment tools, such as Nessus, systematically analyze systems for known flaws, offering essential insights into possible weaknesses.
Web application scanners, like OWASP ZAP, serve as important tools for penetration testing of web applications by specifically targeting them to identify critical security issues such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting, which are prevalent attack vectors. Ultimately, exploitation resources, exemplified by Metasploit, enable testers to exploit identified vulnerabilities, thereby demonstrating the potential impact of these weaknesses. The necessity of utilizing efficient assessment instruments is highlighted by concerning data; for example, the healthcare industry experienced 33% of all third-party assaults in 2021, with ransomware being the predominant technique at 27%.
Moreover, human error accounted for 95% of cybersecurity breaches, highlighting the need for robust security measures. As Caroline Wong, Chief Strategy Officer at Cobalt, highlights, 'updating conventional security assessments through innovative resources and community-driven knowledge is crucial in this swiftly changing environment.' This viewpoint is especially significant as we look forward to 2024, where grasping the most recent developments in security scanning technology and the most widely used testing resources by organizations will be essential for e-commerce directors seeking to improve their cybersecurity stance.
The case study titled 'Statistics That Indicate the Need For Security Testing' further illustrates this necessity, revealing the significant weaknesses faced by the healthcare sector and the critical role of security assessments in safeguarding sensitive information.
Top Tools for Effective Web Application Penetration Testing
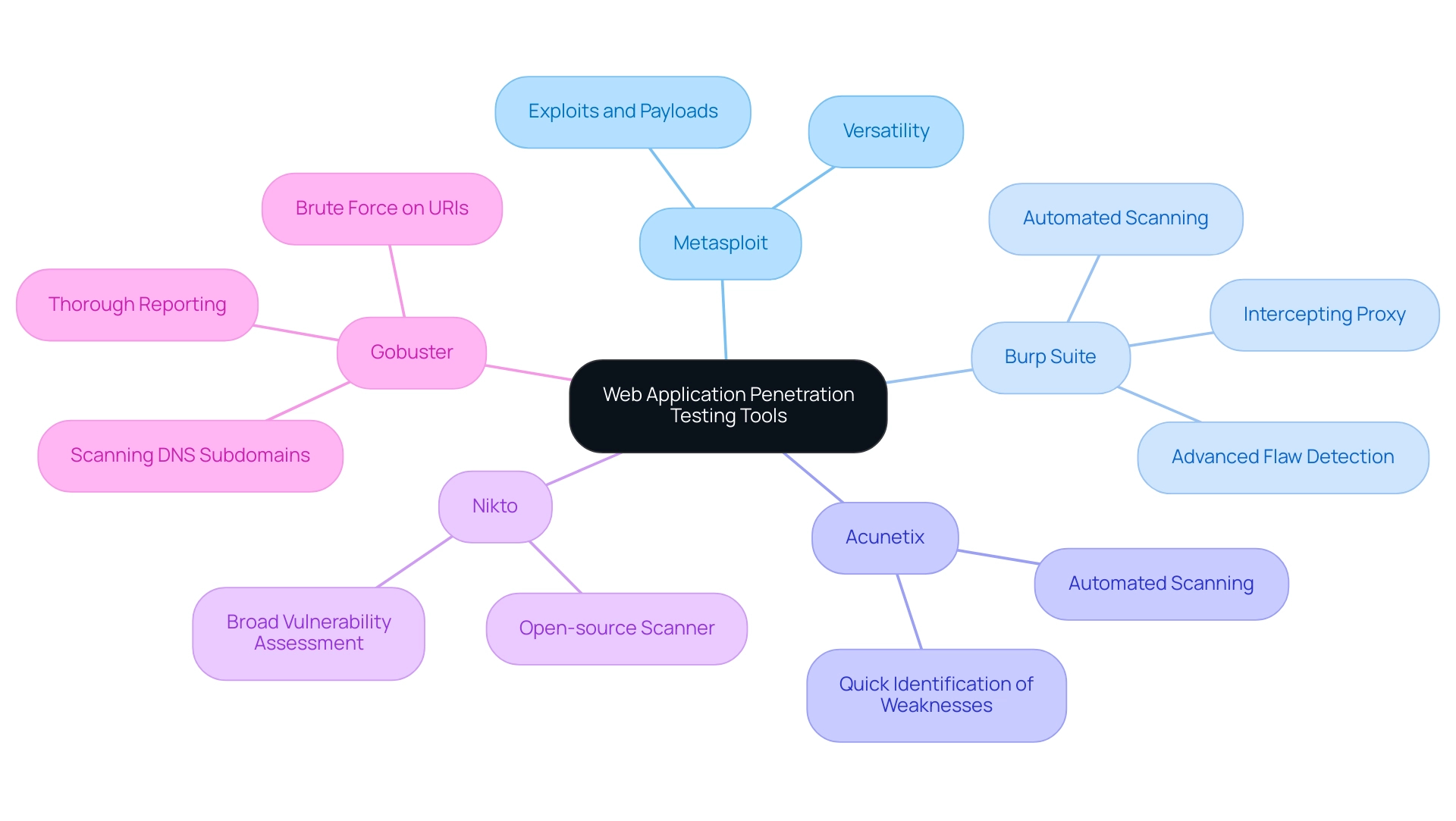
In the constantly changing environment of web application protection, several tools for penetration testing of web applications have emerged as essential for efficiently testing vulnerabilities. Metasploit stands out as a premier framework, offering a vast array of exploits and payloads that empower penetration testers to simulate attacks and detect weaknesses. Its versatility makes it a top choice among protection professionals.
Similarly, Burp Suite has gained popularity for its comprehensive suite of tools for penetration testing of web applications. Its features comprise an intercepting proxy, automated scanning resources, and advanced flaw detection, rendering it essential for comprehensive evaluations.
Acunetix is especially recognized as one of the leading tools for penetration testing of web applications, facilitating swift identification of weaknesses with little manual effort. This is essential considering that 40% of weaknesses identified are frequently linked to inadequate protective measures, highlighting the significance of utilizing strong resources to tackle these issues. Moreover, Nikto, an open-source web server scanner, is among the essential tools for penetration testing of web applications, providing critical assessments against a broad spectrum of weaknesses to enable strong risk analysis.
A representative instance of the efficacy of these resources can be observed in the efforts of a research group from the University of California, Santa Barbara, which, in 2013, utilized w3af in their examination of online banking systems. This utility effectively detected multiple weaknesses in major banks' web applications, greatly improving the protective measures implemented.
Moreover, Gobuster acts as a significant testing resource that enables users to perform scanning and brute force on URIs, DNS subdomains, and Virtual Host names on target web servers. It provides thorough reports for vulnerability detection and is fully open-source, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world applications. As organizations continue to prioritize security, utilizing these tools for penetration testing of web applications—Metasploit, Burp Suite, Acunetix, Nikto, and Gobuster—will be vital in effectively identifying and addressing security weaknesses.
Best Practices for Utilizing Penetration Testing Tools
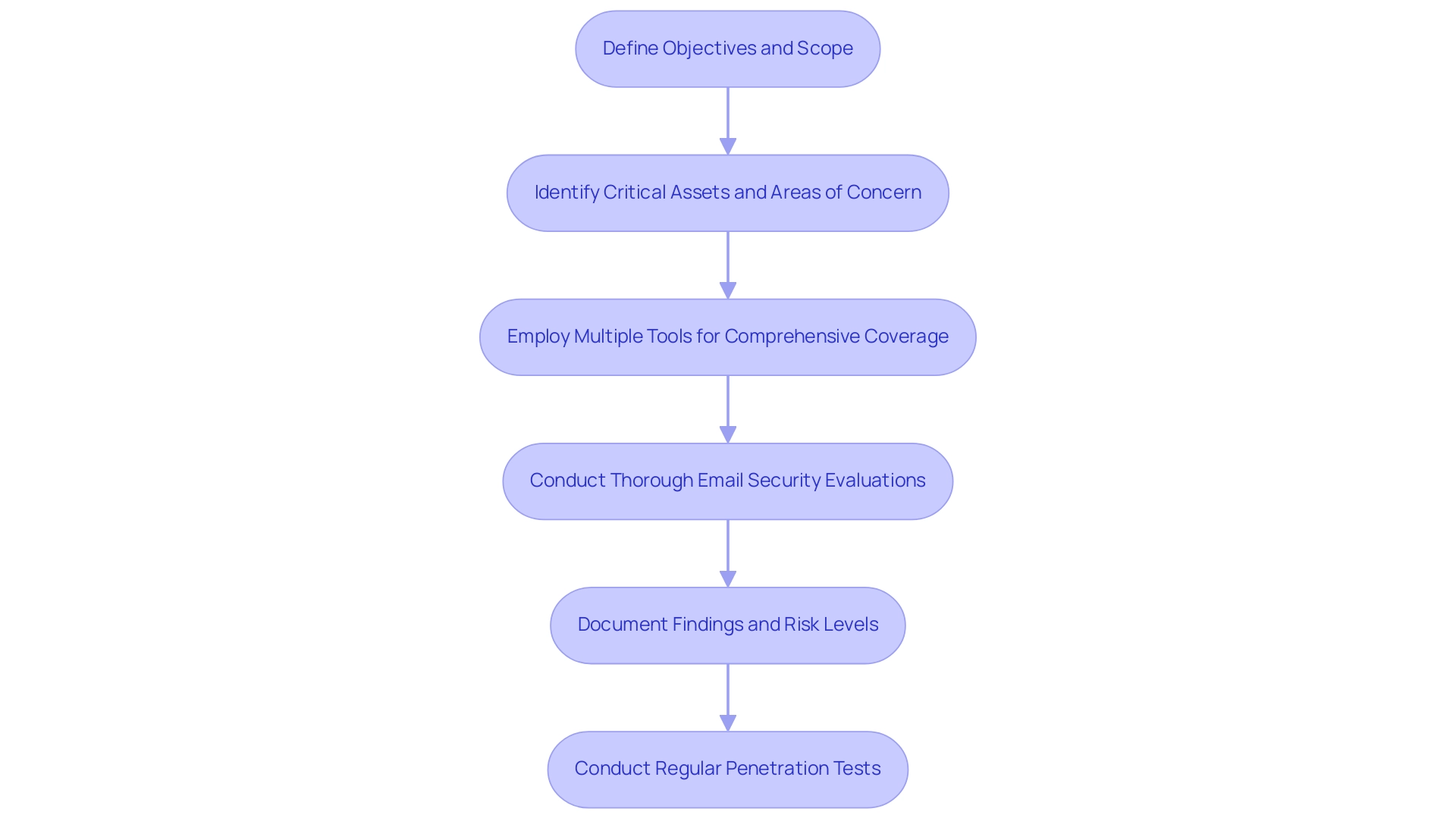
To enhance the efficiency of testing instruments, practitioners should follow several essential best practices. Initially, establishing a structured approach is paramount; this involves defining clear objectives and scope for each security test, including the identification of critical assets and potential areas of concern. It is also essential to ensure comprehensive coverage by employing multiple tools to cross-verify findings, as no single tool can capture all weaknesses.
Given that 92% of malware is delivered via email, a thorough approach becomes even more crucial, particularly for mobile applications, which are increasingly targeted. This emphasizes the need for security testing to include email security evaluations. Documentation of findings should be meticulous, yielding detailed reports that outline identified weaknesses, their associated risk levels, and recommended remediation strategies.
Regular penetration tests are essential, as weaknesses can evolve alongside changes in applications or underlying infrastructure—this is further emphasized by the fact that 70% of cyber crimes targeting financial institutions involve lateral movement. Furthermore, the financial implications of inadequate cybersecurity practices are evident, as 17% of state and local government entities that were hit by cyberattacks chose to pay the ransom. By embracing these best practices, organizations can significantly bolster their security posture, enhancing resilience against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
For instance, the Target data breach in 2013 serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of inadequate cybersecurity practices, as attackers exploited vulnerabilities in point-of-sale systems, affecting approximately 110 million customers and prompting a reevaluation of retail cybersecurity standards. Additionally, an IBM study found that eleven percent of breaches were ransomware attacks, a 7.8% increase from 2021, illustrating the growing threat organizations face. Thus, a structured and proactive approach to penetration testing is not just advisable but essential.
Conclusion
The importance of penetration testing in today's cybersecurity landscape cannot be overstated. As organizations face an increasing number of sophisticated cyber threats, the practice of ethical hacking emerges as a vital strategy for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities. By simulating attacks on web and mobile applications, organizations can proactively uncover weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors, thereby safeguarding sensitive data and preserving their reputations.
Utilizing a diverse array of penetration testing tools, such as Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Acunetix, enhances the ability to detect and address security flaws. Each tool offers unique capabilities that cater to different aspects of web application security, reinforcing the need for a multifaceted approach. Furthermore, understanding the classification of these tools—network scanners, vulnerability scanners, web application scanners, and exploitation tools—empowers security teams to better navigate the complexities of their digital environments.
Adopting best practices for penetration testing is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. Establishing clear objectives, ensuring comprehensive coverage, and maintaining meticulous documentation are foundational steps that enable organizations to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Regular assessments and updates to testing protocols are necessary to adapt to the dynamic nature of vulnerabilities, thus fortifying defenses against potential breaches.
In summary, penetration testing is not merely a preventative measure but an essential component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. Organizations that prioritize ethical hacking and leverage advanced tools and best practices will be better equipped to navigate the challenges of an increasingly perilous digital landscape. The proactive stance taken today can significantly mitigate risks and foster a more secure environment for both businesses and their customers.





