Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) is a transformative technology that is revolutionizing various industries, from museums to education, entertainment to fashion, and even construction. This article explores the diverse applications of AR and its potential to enhance experiences, engage audiences, and improve efficiency.
By seamlessly integrating digital elements into real-world environments, AR offers interactive and immersive experiences that captivate users. Whether it's bringing museum exhibits to life, enhancing storytelling in film and television, reshaping education through interactive learning, transforming the fashion industry with virtual try-ons, or revolutionizing the construction industry with 3D visualization, AR is reshaping the way we perceive and interact with our world. Join us on a journey to discover the limitless possibilities of augmented reality and its impact on various sectors.
Interactive Museum Exhibits with Augmented Reality
Museums have been faced with the profound challenge of balancing the wealth of information they wish to convey with the risk of overwhelming visitors. The solution?
The integration of augmented reality (AR) to enhance exhibits, allowing visitors to interact with artifacts and artworks in a way that brings them to life. Take, for example, the innovative approach by the museum hosting the 'Katharina Grosse.
Studio Paintings, 1988–2022' exhibition, which employed computer vision in their digital guide. This guide provided not only an exhibit map and image previews but also an 'Identify image with camera' feature.
Visitors could simply scan an artwork to unlock a wealth of knowledge, interweaving the digital with the physical realm and enriching the museum experience. Moreover, the recent Art Fund report highlights the urgency for museums to blend physical presence with digital engagement, a necessity underscored when cultural institutions worldwide were forced to shut their doors in 2020. The pivot to digital was not just a stopgap but has become part of a more profound transformation, enhancing the understanding and broadening of audiences. As museums navigate this new landscape, the potential of AR to create immersive, interactive experiences is vast, providing a bridge between the desire for information and the fear of cognitive overload. The technology allows for a seamless continuation of learning, even beyond the walls of the museum, as visitors can bookmark elements to revisit later, ensuring the journey of discovery is unbounded by time or place.
Immersive Storytelling in Film and Television
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing the art of storytelling, particularly in the realms of film and television, where it allows for the seamless integration of digital elements with real-world scenes. A vivid example of this can be seen in BBC's Strictly Come Dancing, where AR has been used to amplify the visual spectacle of dance performances.
Catherine Land, the show's Performance Designer, has been at the forefront of incorporating AR into the show's set design, enhancing the viewers' experience by adding depth to the performances with digitally augmented environments. In the high-stakes world of television production, AR presents an opportunity to construct set designs that not only capture the audience's attention immediately but also leave a lasting impression.
The technology has been instrumental in creating a more immersive viewing experience that complements the show's vibrant choreography, costumes, and music. The entertainment industry's embrace of AR is part of a broader trend.
The AR market is experiencing rapid growth, with significant investments from major companies like Facebook Corporation, Intel Corporation, and Samsung Group, indicating its potential to transform user engagement with digital content in real-world settings. In fact, industries ranging from consumer to healthcare are adopting AR to enhance their operations, with the healthcare sector utilizing immersive modalities to aid medical professionals.
As AR continues to develop, it is also becoming a focal point in discussions about the future of creative jobs, particularly in the context of artificial intelligence's role in content creation. The New York Film and Television Union Coalition has recently expressed strong support for human creativity over AI, highlighting the importance of protecting creative jobs in the industry. This sentiment underscores the need for a balance between technological innovation and the preservation of human-led artistic expression. In conclusion, AR is not just a technological gimmick; it's a powerful tool for enriching narratives and creating engaging, interactive experiences that resonate with audiences. Its potential to add new dimensions to the storytelling process is immense, promising a future where the boundaries between the digital and physical worlds are increasingly blurred.
Augmented Reality in Education
Augmented Reality (AR) is reshaping education, offering a vivid tapestry of interactive and immersive learning experiences that transcend traditional methods. By integrating AR into educational material, such as textbooks and worksheets, students can engage with content in a dynamic way.
For instance, medical students at the University of Edinburgh have benefited from the Anatomy Experience, an AR tool that enhances their understanding of complex bodily structures. This approach not only enriches the learning process but also caters to the diverse learning styles of students.
Bill Gates has noted the obsolescence of textbooks in their traditional form, advocating for the integration of engaging online tools. AR is the embodiment of this vision, merging the tactile appeal of textbooks with the interactive nature of digital media.
With apps like Google Expeditions, students can embark on virtual expeditions, exploring everything from historical sites to natural wonders, all within the confines of the classroom. This experiential learning is backed by research, suggesting that retention rates can soar to 90% when students learn through interactive experiences.
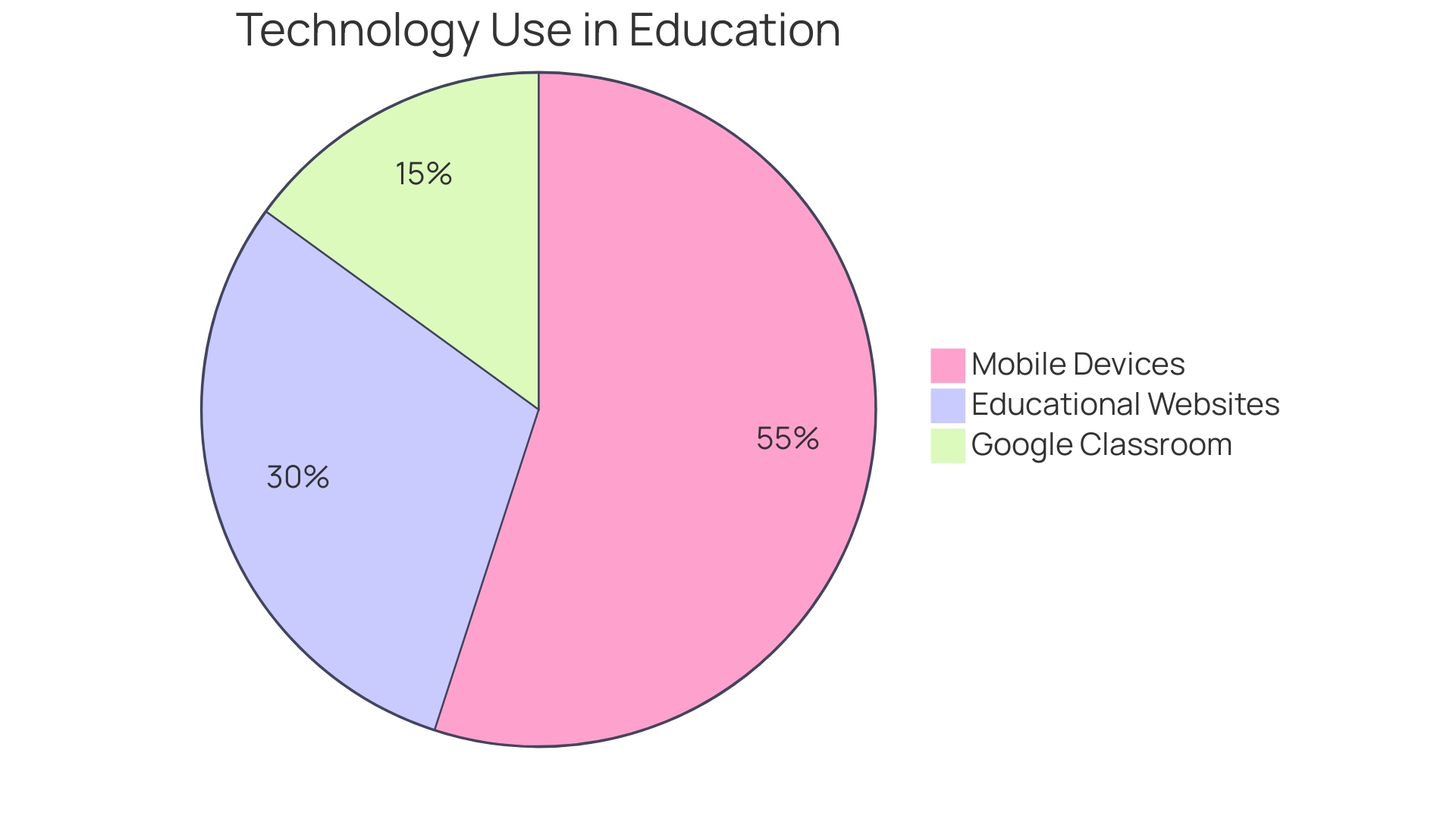
Statistics underscore the significance of technology in education. The human brain processes visuals 60,000 times faster than text, making AR a powerful tool for fast and effective learning. Educators are increasingly adopting technology, with 87% reporting enhanced proficiency with EdTech following school closures in 2020, and 58% viewing technology more favorably. Additionally, 86.5% of K-12 teachers utilize educational websites, and mobile device use in classrooms has risen by 33% between 2015 and 2019. Google Classroom's user base of over 30 million educators and students worldwide further highlights the growing importance of technology in education. These advancements are not just fleeting trends; they represent the dawn of a new era in educational practices, one that promises to equip future generations with the knowledge and skills to flourish in a technologically advanced world.
Virtual Try-On and Interactive Fashion Displays
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming the fashion industry, offering a sustainable alternative to the traditional model of production and consumption. AR allows customers to virtually try on apparel and accessories, alleviating the environmental burden by reducing the need for physical samples. This innovation extends to dazzling, interactive displays that not only captivate shoppers but also encourage mindful purchasing.
For instance, Adobe's interactive dress, showcased by researcher Christine Dierk, exemplifies the potential of AR in fashion. The dress changes patterns at the click of a remote, demonstrating how digital technology can refresh a look instantly without the need for multiple garments. The benefits of AR in retail are multifaceted.
It reduces return rates by enabling customers to visualize the fit and appearance of clothes accurately, leading to more confident purchases. Additionally, AR creates immersive experiences that resonate with consumers, as seen with the viral success of items like Mschf's Big Red Boots and Loewe's playful heels. Despite the fashion industry's growth, with economic profits more than doubling in 2022 compared to the previous decade, the latter half of 2023 saw a decline in consumer spending, indicating a need for innovation to maintain relevance.
As the industry navigates a challenging 2024, AR offers a practical solution for engaging customers and balancing the desire for newness with sustainability. The urgency to adapt is underscored by the climate crisis, with an estimated $65 billion in apparel exports at risk from climate events by 2030. AR not only elevates the shopping experience but also serves as a critical tool for brands to future-proof against environmental and market fluctuations.
Object Recognition in Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing how we interact with our world, blending digital content with real-world environments. In education, for instance, the University of Edinburgh's AR-enhanced 'Anatomy Experience' has dramatically improved medical students' grasp of complex anatomical structures.
This immersive technology has proven more effective than traditional textbooks, enabling interactive, detailed exploration of human anatomy through smartphones or AR glasses. Likewise, the metaverse, a concept still in its infancy, relies on AR for bridging the virtual with the physical.
It's a space where visible and hidden visual markers serve as gateways to digital realms. As we inch closer to a fully-realized metaverse, a unified recognition framework for these markers becomes essential.
In the realm of autonomous navigation, AR's semantic segmentation is critical. Self-driving cars and drones depend on it to detect and navigate through their surroundings safely.
Moreover, AR's capacity to convert 2D images into 3D models is invaluable across architecture, archaeology, and virtual reality. Object recognition is another facet of AR's prowess.
With computer vision models, such as zero-shot and fine-tuned models, AR can identify a multitude of objects, aiding everything from captioning images to analyzing specific items for data. Furthermore, AR enhances hand-object interaction understanding, promising to facilitate skill transfer between humans or even from humans to robots. This feature holds the potential to transform educational, business, and training experiences into more immersive and engaging activities. The technology's adoption is on the rise, with significant investments from tech giants and research institutions alike. Industries ranging from consumer to healthcare are leveraging AR for its ability to provide realistic, interactive experiences that enhance task performance. In essence, AR's object recognition not only overlays digital information onto the physical world but also adds depth and context, transforming how we learn, work, and interact with our environment.
Augmented Reality in Construction
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing the construction industry by enabling the visualization of 3D models in actual environments. This technology facilitates enhanced communication and collaboration, allowing for more informed decision-making.
It's particularly useful in addressing the chronic inefficiencies that have plagued construction projects, such as cost overruns and delays due to rework and downtime. With AR, construction professionals can identify design conflicts early and monitor project progress more effectively, thus reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes.
The Centre for Sensors, Instruments and Systems Development (CD6) at UPC is pioneering the integration of AR with building information modeling (BIM) to create a comprehensive tool across the construction life cycle. This addresses the industry's need for better planning, visualization, and operations management tools.
Despite the potential of AR to improve productivity, its adoption has been slow, hindered by technical limitations of AR devices. However, the urgency for change is clear: the construction industry could save up to $1.7 trillion by 2030 through automation and AR, as reported by the World Economic Forum.
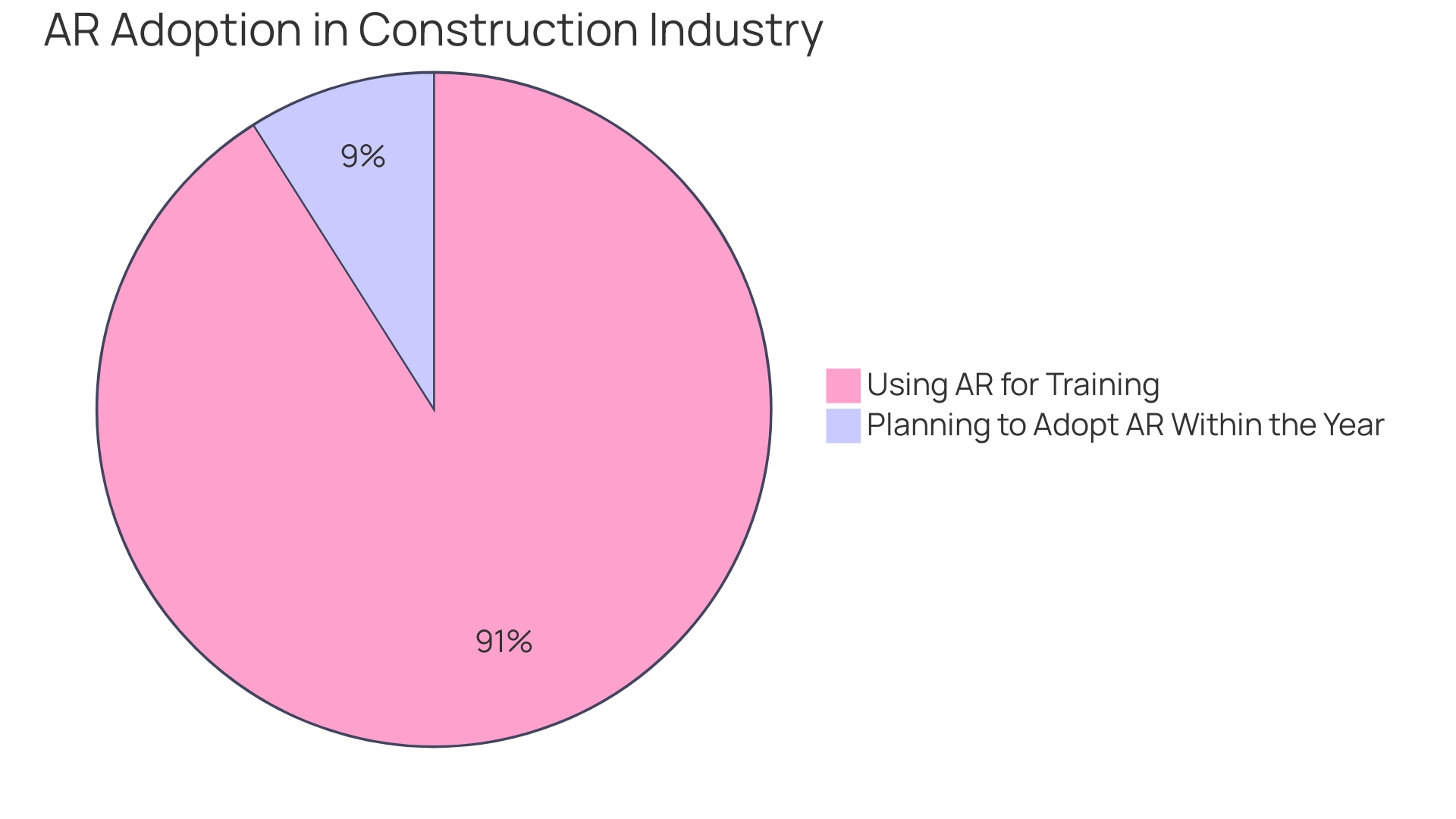
Senior executives in construction are encouraged to conduct assessments for potential automation and collaborate with technology providers to tailor solutions that can enhance productivity and safety on-site. Moreover, AR's potential isn't limited to cost savings. As Peggy Smedley notes, the technology can mitigate risks and expedite construction processes. Market research by SkyQuest anticipates a 44.5% growth in the AR market by 2030, with construction identified as a key sector to benefit from these advancements. The statistics are compelling—47% of professionals are using or piloting AR for training, with another 21% planning to do so within the year. This indicates a growing recognition of AR as a valuable tool for workforce development and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing industries like museums, film and television, education, fashion, object recognition, and construction. AR enhances museum experiences by allowing interactive engagement with exhibits. It amplifies storytelling in film and television through seamless integration of digital elements.
In education, AR provides immersive learning experiences that cater to diverse styles and improve retention rates. The fashion industry benefits from virtual try-on experiences and interactive displays. Object recognition in AR transforms various sectors by adding depth and context to interactions.
In construction, AR enables visualization of 3D models for better communication and decision-making. Overall, AR is a powerful tool for enriching narratives and creating engaging experiences that bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Its potential for innovation and transformation across industries is immense.
Experience the power of Augmented Reality (AR) for yourself and revolutionize your industry today!





